SBOS629A April 2018 – July 2018 OPA858
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DSG|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DSG|8
Orderable Information
9.3.4 Slew Rate and Output Stage
In addition to wide bandwidth, the OPA858 features a high slew rate of 2000 V/µs . The slew rate is a critical parameter in high-speed pulse applications with narrow sub 10-ns pulses such as Optical Time-Domain Reflectometry (OTDR) and LIDAR. The high slew rate of the OPA858 implies that the device accurately reproduces a 2-V, sub-ns pulse edge as seen in Figure 20. The wide bandwidth and slew rate of the OPA858 make it an ideal amplifier for high-speed, signal-chain front ends.
Figure 52 shows the open-loop output impedance of the OPA858 as a function of frequency. To achieve high slew rates and low output impedance across frequency, the output swing of the OPA858 is limited to approximately 3 V. The OPA858 is typically used in conjunction with high-speed pipeline ADCs and flash ADCs that have limited input ranges. Therefore, the OPA858 output swing range coupled with the class-leading voltage noise specification maximizes the overall dynamic range of the signal chain.
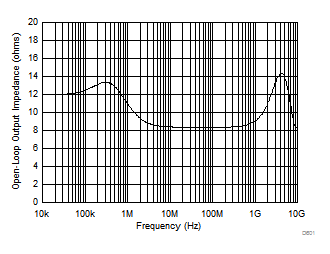 Figure 52. Open-Loop Output Impedance (ZOL) vs Frequency
Figure 52. Open-Loop Output Impedance (ZOL) vs Frequency