SLLSFI7 October 2020 SN65HVD64
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGT|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGT|16
Orderable Information
8.4 Device Functional Modes
If DIRSET1 and DIRSET2 are in a logic high state, the device will be in standby mode. While in standby mode, the receiver functions normally, detecting carrier frequency activity on the RXIN pin and setting the RXOUT state. The transmitter circuits are not active in standby mode, thus the TXOUT pin is idle regardless of the logic state of TXIN. The supply current in standby mode is significantly reduced, allowing power savings when the node is not transmitting.
When not in standby mode, the default power-on state is idle. When in idle mode, RXOUT is high, and TXOUT is quiet. The device transitions to receive mode when a valid modulated signal is detected on the RXIN line or the device transitions to transmit mode when TXIN goes low. The device stays in either receive or transmit mode until DIR time-out (nominal 16 bit times) after the last activity on RXOUT or TXIN.
When in receive mode:
- RXOUT responds to all valid modulated signals on RXIN, whether from the local transmitter, a remote transmitter, or long noise burst.
- TXOUT responds to TXIN, generating 2.176-MHz signals on TXOUT when TXIN is low, and TXOUT is quiet when TXIN is high. (In normal operation, TXIN is expected to remain high when the device is in receive mode.)
- The device stays in receive mode until 16 bit times after the last rising edge on RXOUT, caused by valid modulated signal on the RXIN line.
When in transmit mode:
- RXOUT stays high, regardless of the input signal on RXIN.
- TXOUT responds to TXIN, generating 2.176-MHz signals on TXOUT when TXIN is low, and TXOUT is quiet when TXIN is high.
- The device stays in transmit mode until 16 bit times after TXIN goes high.
Table 8-1 shows the driver functions. Table 8-2 shows the receiver functions. Figure 8-1 shows the transitions between each state.
| TXIN(1) | [DIRSET1, DIRSET2] | TXOUT | COMMENT |
|---|---|---|---|
| H | [L,L], [L,H] or [H,L] | < 1 mVPP at 2.176 MHz | Driver not active |
| L | VOPP at 2.176 MHz | Driver active | |
| X | [H,H] | < 1 mVPP at 2.176 MHz | Standby mode |
| RXIN(1) | RXOUT | DIR | COMMENT (see Figure 8-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IDLE mode (not transmitting or receiving) | |||
| < VIT at 2.176 MHz for longer than DIR time-out | H | L | No outgoing or incoming signal |
| RECEIVE mode (not already transmitting) | |||
| < VIT at 2.176 MHz for less than tDIR time-out | H | H | Incoming 1 bit, DIR stays HIGH for DIR time-out |
| > VIT at 2.176 MHz for longer than tnoise filter | L | H | Incoming 0 bit, DIR output is HIGH |
| TRANSMIT mode (not already receiving) | |||
| X | H | L | Outgoing message, DIR stays LOW for DIR time-out |
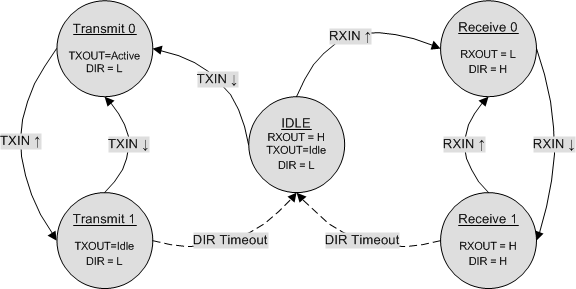 Figure 8-1 State Transition Diagram
Figure 8-1 State Transition Diagram