SLLSEH3C July 2013 – January 2018 SN65HVD888
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
(see (1))| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage | –0.5 | 7 | V | |
| Input voltage at any logic pin | –0.3 | 5.7 | V | ||
| Voltage input, transient pulse, A and B, through 100 Ω | –100 | 100 | V | ||
| Voltage at A or B inputs | –18 | 18 | V | ||
| Receiver output current | –24 | 24 | mA | ||
| Continuous total-power dissipation | See (Thermal Information) table | ||||
| TJ | Junction temperature | 170 | °C | ||
| TSTG | Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
6.2 ESD Ratings: JEDEC Specifications
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±8000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1500 | |||
| Machine model (MM) | ±100 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 ESD Ratings: IEC Specifications
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | IEC 61000-4-2 ESD (Contact Discharge), bus terminals and GND | ±12000 | V |
| IEC 61000-4-4 EFT (Fast transient or burst) bus terminals and GND | ±4000 | |||
| IEC 60749-26 ESD (HBM), bus terminals and GND | ±16000 | |||
6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage | 4.5 | 5 | 5.5 | V | |
| VID | Differential input voltage | –12 | 12 | V | ||
| VI | Input voltage at any bus terminal (separate or common mode)(1) | –7 | 12 | V | ||
| VIH | High-level input voltage (driver, driver-enable, and receiver-enable inputs) | 2 | VCC | V | ||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage (driver, driver-enable, and receiver-enable inputs) | 0 | 0.8 | V | ||
| IO | Output current | Driver | –60 | 60 | mA | |
| Receiver | –8 | 8 | ||||
| CL | Differential load capacitance | 50 | pF | |||
| RL | Differential load resistance | 60 | Ω | |||
| 1/tUI | Signaling rate | 0.3 | 250 | kbps | ||
| TJ | Junction temperature | –40 | 150 | °C | ||
| TA(2) | Operating free-air temperature (see Thermal Information for additional information) | –40 | 125 | °C | ||
(1) The algebraic convention in which the least positive (most negative) limit is designated as minimum is used in this data sheet.
(2) Operation is specified for internal (junction) temperatures up to 150°C. Self-heating due to internal power dissipation should be considered for each application. Maximum junction temperature is internally limited by the thermal shut-down (TSD) circuit which disables the driver outputs when the junction temperature reaches 170°C.
6.5 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | SN65HVD888 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| D (SOIC) | |||
| 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 116.1 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 60.8 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 57.1 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 13.9 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 56.5 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
6.6 Electrical Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| │VOD│ | Driver differential-output voltage magnitude | RL = 60 Ω, 375 Ω on each output from –7 to +12 V | See Figure 4 | 1.5 | 2.5 | V | |
| RL = 54 Ω (RS-485) | See Figure 5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | ||||
| RL = 100 Ω (RS-422) | 2 | 3 | |||||
| Δ│VOD│ | Change in magnitude of driver differential-output voltage | RL = 54 Ω, CL = 50 pF | See Figure 5 | –0.2 | 0 | 0.2 | V |
| VOC(SS) | Steady-state common-mode output voltage | Center of two 27-Ω load resistors | See Figure 5 | 1 | VCC / 2 | 3 | V |
| ΔVOC | Change in differential driver common-mode output voltage | Center of two 27-Ω load resistors | See Figure 5 | –0.2 | 0 | 0.2 | mV |
| VOC(PP) | Peak-to-peak driver common-mode output voltage | Center of two 27-Ω load resistors | See Figure 5 | 850 | mV | ||
| COD | Differential output capacitance | 8 | pF | ||||
| VIT+ | Positive-going receiver differential-input voltage threshold | 35 | 100 | mV | |||
| VIT– | Negative-going receiver differential-input voltage threshold | –100 | –35 | mV | |||
| VHYS(1) | Receiver differential-input voltage threshold hysteresis (VIT+ – VIT– ) | 40 | 60 | mV | |||
| VOH | Receiver high-level output voltage | IOH = –8 mA | 2.4 | VCC – 0.3 | V | ||
| VOL | Receiver low-level output voltage | IOL = 8 mA | 0.2 | 0.4 | V | ||
| II | Driver input, driver enable, and receiver enable input current | –2 | 2 | µA | |||
| IOZ | Receiver high-impedance output current | VO = 0 V or VCC, RE at VCC | –10 | 10 | µA | ||
| │IOS│ | Driver short-circuit output current | │IOS│ with VA or VB from –7 to +12 V | 150 | mA | |||
| II | Bus input current (driver disabled) | VCC = 4.5 to 5.5 V or | VI = 12 V | 75 | 125 | µA | |
| VCC = 0 V, DE at 0 V | VI = –7 V | –100 | –40 | ||||
| ICC | Supply current (quiescent) –40°C to 85°C |
Driver and receiver enabled | DE = VCC, RE = GND, No load |
750 | 900 | µA | |
| Driver enabled, receiver disabled | DE = VCC, RE = VCC, No load |
650 | |||||
| Driver disabled, receiver enabled | DE = GND, RE = GND, No load |
750 | |||||
| Driver and receiver disabled | DE = GND, D = GND RE = VCC, No load |
0.4 | 5 | ||||
| ICC | Supply current (quiescent) –40°C to 125°C |
Driver and receiver enabled | DE = VCC, RE = GND, No load |
750 | 990 | µA | |
| Driver enabled, receiver disabled | DE = VCC, RE = VCC, No load |
715 | |||||
| Driver disabled, receiver enabled | DE = GND, RE = GND, No load |
825 | |||||
| Supply current (dynamic) | See Figure 3 | ||||||
(1) Under any specific conditions, VIT+ is specified to be at least VHYS higher than VIT–.
6.7 Power Dissipation Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD | Power Dissipation driver and receiver enabled, VCC = 5.5 V, TJ = 150°C 50% duty cycle square-wave signal at 250 kbps signaling rate: |
Unterminated | RL = 300 Ω, CL = 50 pF (driver) |
164 | mW | |
| RS-422 load | RL = 100 Ω, CL = 50 pF (driver) |
247 | ||||
| RS-485 load | RL = 54 Ω, CL = 50 pF (driver) |
316 | ||||
6.8 Switching Characteristics
3.3 ms > bit time > 4 μs (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRIVER | |||||||
| tr, tf | Driver differential-output rise and fall times | RL = 54 Ω, CL = 50 pF | See Figure 6 | 400 | 700 | 1200 | ns |
| tPHL, tPLH | Driver propagation delay | RL = 54 Ω, CL = 50 pF | See Figure 6 | 90 | 700 | 1000 | ns |
| tSK(P) | Driver pulse skew, |tPHL – tPLH| | RL = 54 Ω, CL = 50 pF | See Figure 6 | 25 | 200 | ns | |
| tPHZ, tPLZ | Driver disable time | See Figure 7 and Figure 8 | 50 | 500 | ns | ||
| tPHZ, tPLZ | Driver enable time | Receiver enabled | See Figure 7 and Figure 8 | 500 | 1000 | ns | |
| Receiver disabled | See Figure 7 and Figure 8 | 3 | 9 | µs | |||
| RECEIVER | |||||||
| tr, tf | Receiver output rise and fall times | CL = 15 pF | See Figure 9 | 18 | 30 | ns | |
| tPHL, tPLH | Receiver propagation delay time | CL = 15 pF | See Figure 9 | 85 | 195 | ns | |
| tSK(P) | Receiver pulse skew, |tPHL – tPLH| | CL = 15 pF | See Figure 9 | 1 | 15 | ns | |
| tPHZ, tPLZ | Receiver disable time | 50 | 500 | ||||
| tPZL(1), tPZH(1)
tPZL(2), tPZH(2) |
Receiver enable time | Driver enabled | See Figure 10 | 20 | 130 | ns | |
| Driver disabled | See Figure 11 | 2 | 8 | µs | |||
| tFS | Bus failsafe time | Driver disabled | See Figure 12 | 44 | 58 | 76 | ms |
6.9 Typical Characteristics
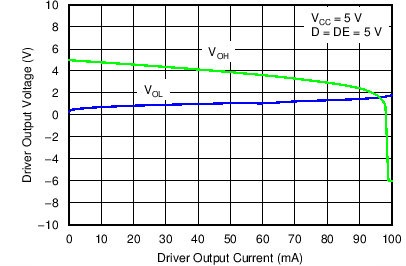 Figure 1. Driver Output Voltage vs Driver Output Current
Figure 1. Driver Output Voltage vs Driver Output Current
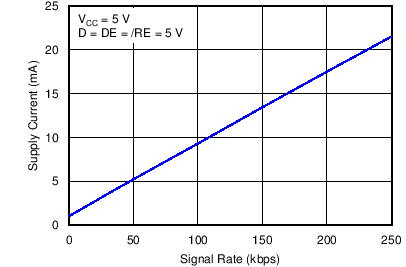 Figure 3. Supply Current vs Signaling Rate
Figure 3. Supply Current vs Signaling Rate
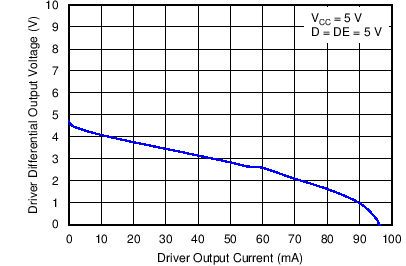 Figure 2. Driver Differential Output Voltage vs Driver Output Current
Figure 2. Driver Differential Output Voltage vs Driver Output Current