SLLSFE2 June 2019 SN65HVDA1040B-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
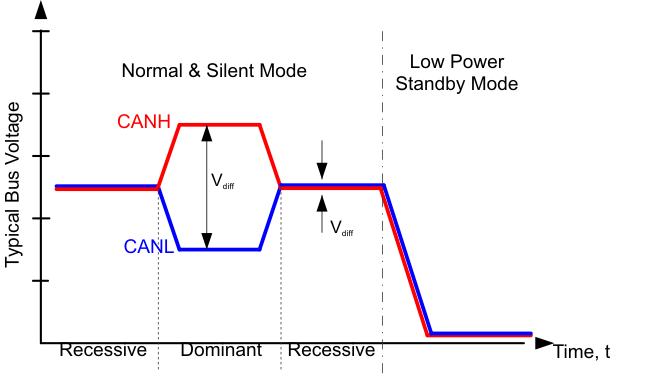
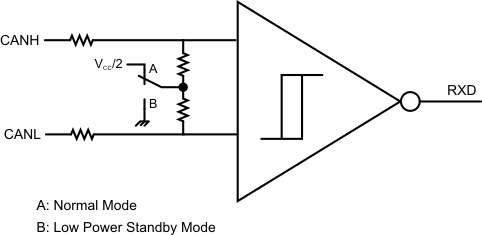
8.3.1.1 Bus States by Mode
The CAN bus has three valid states during powered operation depending on the mode of the device. In normal mode the bus may be dominant (logic low) where the bus lines are driven differentially apart or recessive (logic high) where the bus lines are biased to VCC/2 through the high-ohmic internal input resistors RIN of the receiver. The third state is low-power standby mode where the bus lines is biased to GND through the high-ohmic internal input resistors RIN of the receiver.