SLLS530C April 2002 – February 2019 SN65LVDT14 , SN65LVDT41
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Receiver Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Driver Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 Device Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8 Receiver Switching Characteristics
- 6.9 Driver Switching Characteristics
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PW|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PW|20
Orderable Information
11.1.1 Microstrip vs. Stripline Topologies
As per the LVDS application and data handbook (SLLD009), printed-circuit boards usually offer designers two transmission line options: microstrip and stripline. Microstrips are traces on the outer layer of a PCB, as shown in Figure 23.
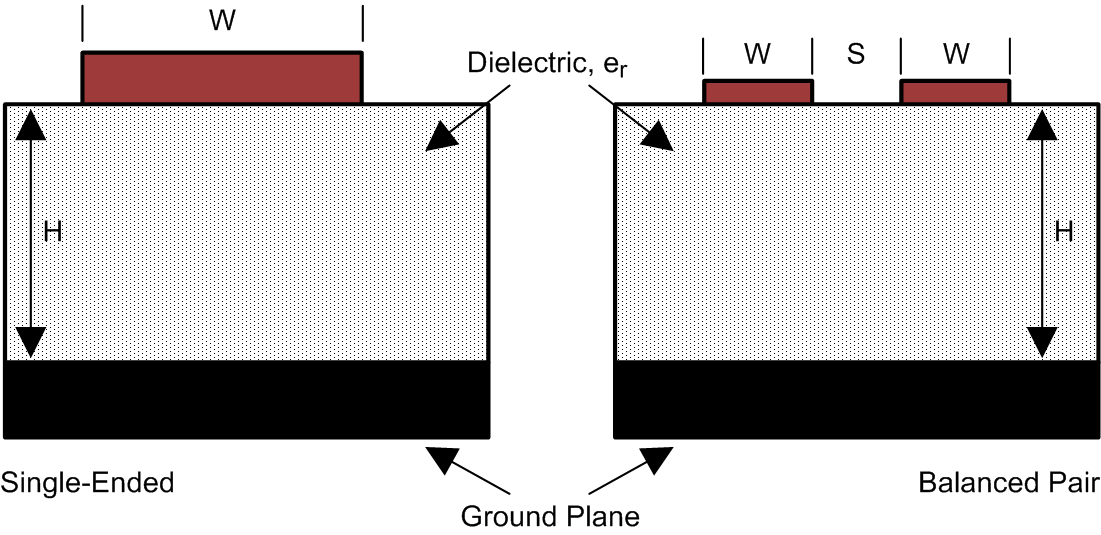 Figure 23. Microstrip Topology
Figure 23. Microstrip Topology On the other hand, striplines are traces between two ground planes. Striplines are less prone to emissions and susceptibility problems because the reference planes effectively shield the embedded traces. However, from the standpoint of high-speed transmission, juxtaposing two planes creates additional capacitance. TI recommends routing LVDS signals on microstrip transmission lines when possible. The PCB traces allow designers to specify the necessary tolerances for ZO based on the overall noise budget and reflection allowances. Footnotes 1(2), 2(3), and 3(4) provide formulas for ZO and tPD for differential and single-ended traces. (2)(3)(4)
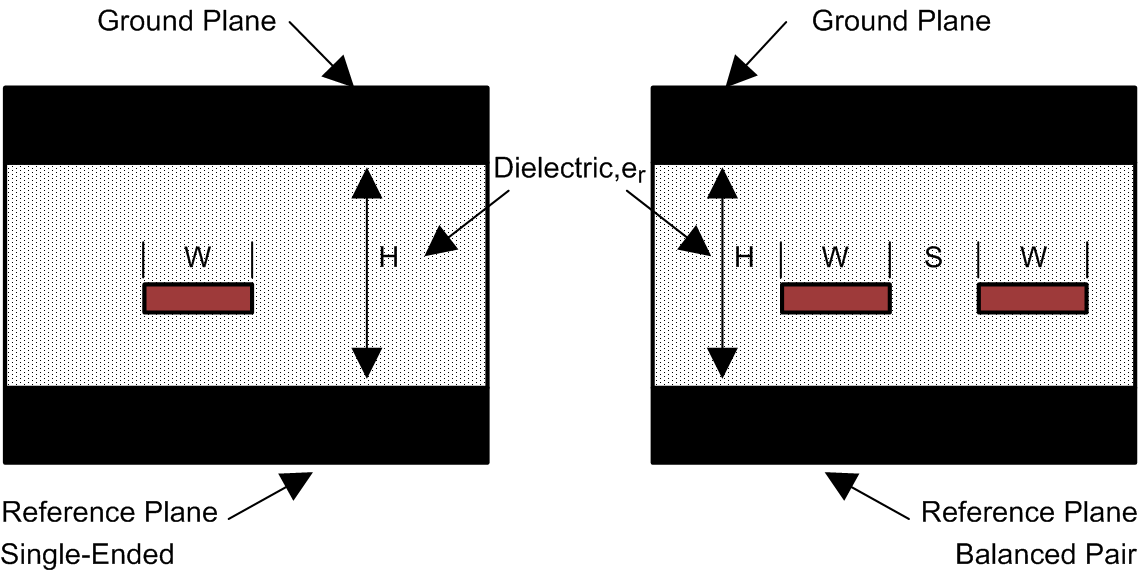 Figure 24. Stripline Topology
Figure 24. Stripline Topology