SCPS272C October 2019 – January 2021 TCA9511A
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application Information Disclaimer
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGK|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DGK|8
Orderable Information
9.2.1.1 Series connections
It is possible to have multiple buffers in series, but care must be taken when designing a system.
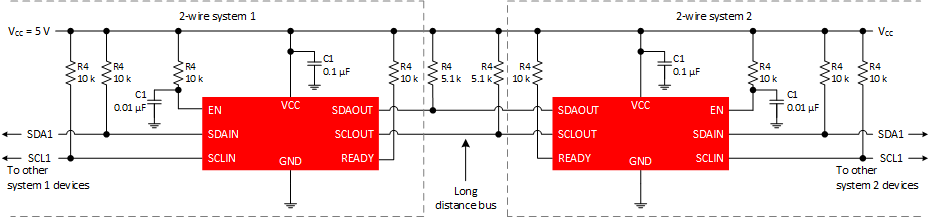 Figure 9-2 Series Buffer Connections
Figure 9-2 Series Buffer ConnectionsEach buffer adds approximately 60 mV of offset. Maximum offset (VOFFSET) should be considered. The low level at the signal origination end is dependent upon bus load. The I2C-bus specification requires that a 3 mA current produces no larger than a 0.4 V VOL. As an example, if the VOL at the master is 0.1 V, and there are 4 buffers in series (each adding about 60 mV), then the VOL at the farthest buffer is approximately 0.34 V. This device has a rise time accelerator (RTA) that activates at 0.6 V. With great care, a system with 4 buffers may work, but as the VOL moves up, it may be possible to trigger the RTA, creating a false edge on the clock.
It is recommended to limit the number of buffers in series to two, and to keep the load light to minimize the offset.
Another special consideration of series connections is the effect on round-trip-delay. This is the sum of propagation delays through the buffers and any effects on rise time. It is possible that fast mode speeds (400 kHz) are not possible due to delays and bus loading.