SCPS207G May 2012 – November 2019 TCA9548A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGE|24
Orderable Information
8.5.3.1 Writes
To write on the I2C bus, the master sends a START condition on the bus with the address of the slave, as well as the last bit (the R/W bit) set to 0, which signifies a write. The slave acknowledges, letting the master know it is ready. After this, the master starts sending the control register data to the slave until the master has sent all the data necessary (which is sometimes only a single byte), and the master terminates the transmission with a STOP condition.
There is no limit to the number of bytes sent, but the last byte sent is what is in the register.
Figure 10 shows an example of writing a single byte to a slave register.
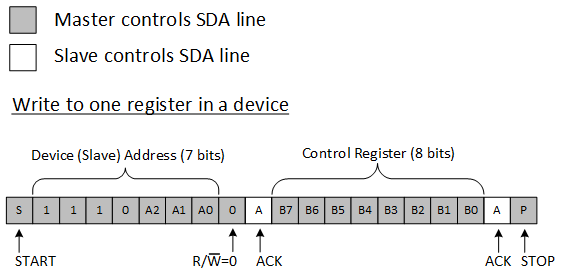 Figure 10. Write to Register
Figure 10. Write to Register