SLOS318L april 2000 – august 2023 THS4130 , THS4131
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.4.1.1 PowerPAD™ Integrated Circuit Package Design Considerations
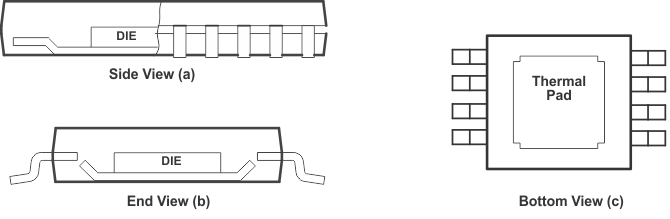
The THS413x is available in a thermally-enhanced DGN package, which is a member of the PowerPAD™ integrated circuit package family. This package is constructed using a downset leadframe upon which the die is mounted (see Figure 9-7a and Figure 9-7b). This arrangement results in the lead frame being exposed as a thermal pad on the underside of the package (see Figure 9-7c). Because this thermal pad has direct thermal contact with the die, excellent thermal performance can be achieved by providing a good thermal path away from the thermal pad.
The PowerPAD package allows for both assembly and thermal management in one manufacturing operation. During the surface-mount solder operation (when the leads are being soldered), the thermal pad can also be soldered to a copper area underneath the package. Through the use of thermal paths within this copper area, heat can be conducted away from the package into either a ground plane or other heat dissipating device.
The PowerPAD package represents a breakthrough in combining the small area and ease of assembly of the surface mount with the previously awkward mechanical methods of using a heat sink.
More complete details of the PowerPAD installation process and thermal management techniques can be found in PowerPAD Thermally-Enhanced Package application report. This document can be found on the TI website at www.ti.com by searching for the keyword PowerPAD. The document can also be ordered through your local TI sales office; refer to SLMA002 when ordering.