SLLSF79B April 2021 – September 2021 THVD1439 , THVD1439V , THVD1449 , THVD1449V
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 ESD Ratings, IEC
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Power Dissipation
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8 Switching Characteristics (THVD1439, THVD1439V)
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics (THVD1449, THVD1449V)
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.1 Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Protection
The bus pins of the THVD14x9(V) transceiver family include on-chip ESD protection against ±15-kV HBM and ±15-kV IEC 61000-4-2 contact discharge. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) ESD test is far more severe than the HBM ESD test. The 50% higher charge capacitance, C(S), and 78% lower discharge resistance, R(D), of the IEC model produce significantly higher discharge currents than the HBM model. As stated in the IEC 61000-4-2 standard, contact discharge is the preferred transient protection test method.
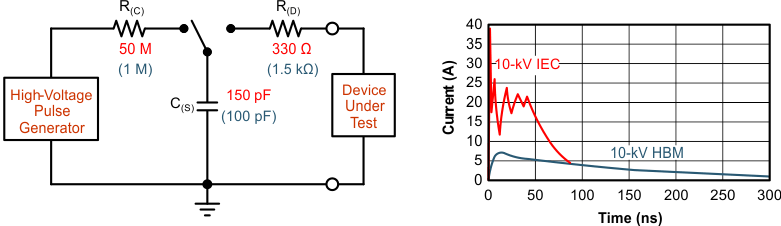 Figure 8-3 HBM and IEC ESD Models and Currents in Comparison (HBM Values in Parenthesis)
Figure 8-3 HBM and IEC ESD Models and Currents in Comparison (HBM Values in Parenthesis)The on-chip implementation of IEC ESD protection significantly increases the robustness of equipment. Common discharge events occur because of human contact with connectors and cables.