SLVSE13H September 2017 – July 2021 TLV7031 , TLV7032 , TLV7034 , TLV7041 , TLV7042 , TLV7044
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information (Single)
- 6.5 Thermal Information (Dual)
- 6.6 Thermal Information (Quad)
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics (Single)
- 6.8 Switching Characteristics (Single)
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics (Dual)
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics (Dual)
- 6.11 Electrical Characteristics (Quad)
- 6.12 Switching Characteristics (Quad)
- 6.13 Timing Diagrams
- 6.14 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.4.2 Detailed Design Procedure
First, choose a target range of hysteresis to achieve. For this design example, 50mV of hysteresis will be the target. Since the TLV7032 already has 10mV (typ) of internal hysteresis, the voltage output from the TMR Rotation Sensor should be scaled down by a factor of 5. This way, the 10mV of internal hysteresis gets scaled up by a factor of 5, resulting in 50mV of hysteresis. The minimum output HIGH level for the TMR Rotation Sensor used in Figure 47 is 5.25 V. Since 5.25V will be the minimum output high value, it can be used to substitute VIN from the Voltage Divider Equation in Figure 48. Since the voltage from the TMR rotation sensor needs to be scaled down by a factor of 5, the equation in Figure 48 can be rewritten as:
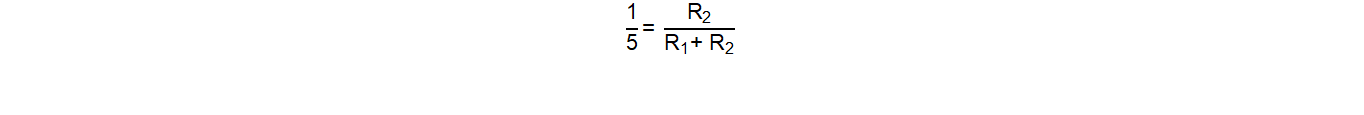 The above equation can be solved for using standard resistor values, where R1 = 100kΩ, and R2 = 24.9kΩ. The minimum voltage seen at the noninverting pins of the comparator when the output is HIGH will be 1.05V. To make the device transition at 50% output high level, the inverting pins of the TLV7032 should be tied to a 0.525V reference.
The above equation can be solved for using standard resistor values, where R1 = 100kΩ, and R2 = 24.9kΩ. The minimum voltage seen at the noninverting pins of the comparator when the output is HIGH will be 1.05V. To make the device transition at 50% output high level, the inverting pins of the TLV7032 should be tied to a 0.525V reference.