SBOS994E November 2019 – January 2022 TLV9351 , TLV9352 , TLV9354
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application Information Disclaimer
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.4 Thermal Protection
The internal power dissipation of any amplifier causes its internal (junction) temperature to rise. This phenomenon is called self heating. The absolute maximum junction temperature of the TLV935x is 150°C. Exceeding this temperature causes damage to the device. The TLV935x has a thermal protection feature that prevents damage from self heating. The protection works by monitoring the temperature of the device and turning off the op amp output drive for temperatures above 140°C. Figure 7-4 shows an application example for the TLV9351 that has significant self heating (159°C) because of its power dissipation (0.81 W). Thermal calculations indicate that for an ambient temperature of 65°C the device junction temperature must reach 187°C. The actual device, however, turns off the output drive to maintain a safe junction temperature. Figure 7-4 shows how the circuit behaves during thermal protection. During normal operation, the device acts as a buffer so the output is 3 V. When self heating causes the device junction temperature to increase above 140°C, the thermal protection forces the output to a high-impedance state and the output is pulled to ground through resistor RL.
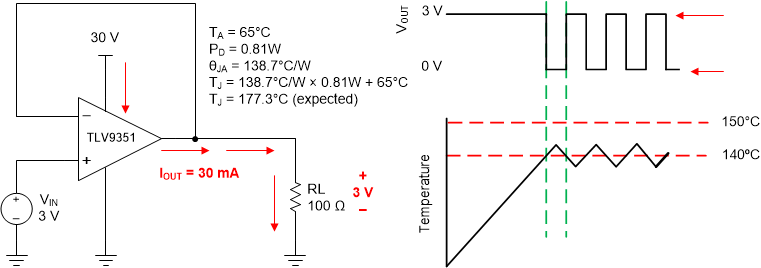 Figure 7-4 Thermal Protection
Figure 7-4 Thermal Protection