SBOS820C September 2019 – June 2025 TMCS1100
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.4 External Reference Voltage Input
The reference voltage provided externally to the TMCS1100 on the VREF pin determines the zero current output voltage, VOUT,0A. This zero-current output level along with sensitivity determine the measurable input current range of the device, and allows for unidirectional or bidirectional sensing, as described in the Absolute Maximum Ratings table. Figure 8-12 illustrates the transfer function of the TMCS1100A2 with varying VREF voltages of 0V, 1.25V, and 2.5V. By shifting the zero current output voltage of the device, the dynamic range of measurable input current can be modified.
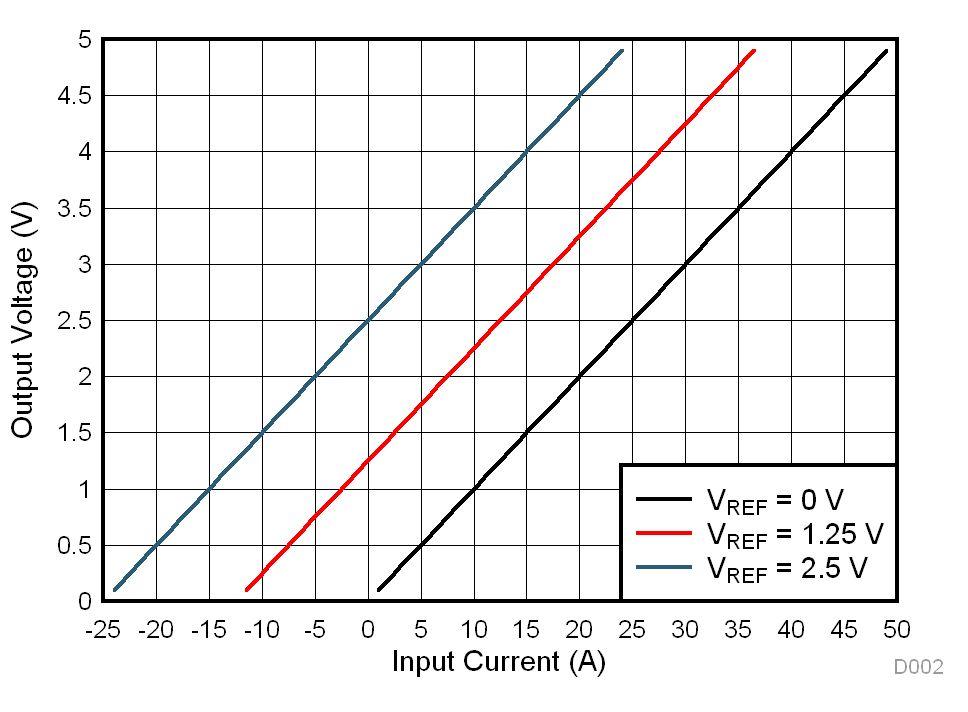 Figure 8-12 Output Voltage Relationship to Input Current With Varying VREF Voltages
Figure 8-12 Output Voltage Relationship to Input Current With Varying VREF VoltagesThe input voltage on this pin can be provided by any external voltage source or potential, such as a discrete precision reference, a voltage divider, ADC reference, or ground. The VREF pin is sampled by the internal circuitry at approximately 1MHz, then buffered and provided to the signal chain of the device. An apparent DC load of approximately 1µA is observed by the external reference. To prevent errors due to sampling settling, keep the source impedance below the level specified in the Electrical Characteristics table.