SNIS214E june 2021 – july 2023 TMP114
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YMT|4
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.3 Temperature Limits
TMP114 includes an on-board temperature limit warning. At the end of every completed conversion, the TMP114 compares the result against the limits stored in the low limit register and the high limit register. When the results exceed the THigh_Limit register value, the THigh_Status and THigh_Flag bits are set. Upon read, the THigh_Flag will clear but the THigh_Status bit will remain set. After the measured temperature crosses below the THigh_Limit - THigh_Hyst value, the THigh_Status bit will clear and the THigh_Flag bit is set again to indicate a change in the temperature with respect to the limits.
If the controller is unable to read the Temp_Result register for a prolonged period of time, the flag bits can be used to determine if a thermal limit was crossed during that time. The flag bits will only clear after a successful Alert_Status register read, therefore the high and low flags can help determine if the system crossed the thermal limit before an I2C read could be performed. The Status bits will automatically update with changing Temp_Result values. Figure 8-1 depicts this behavior.
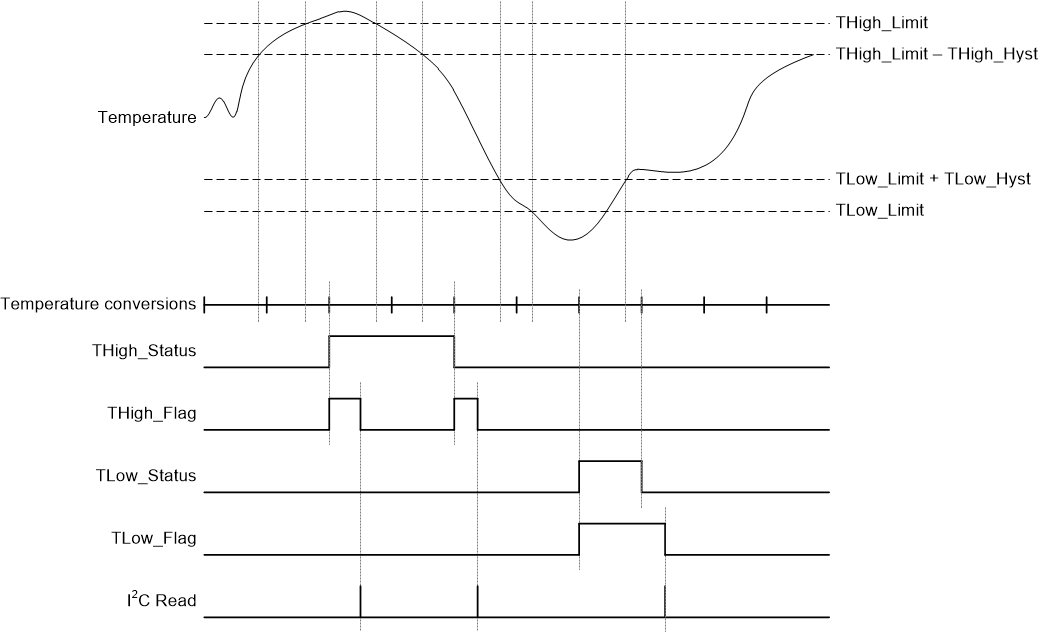 Figure 8-1 Alert Status Timing Diagram
Figure 8-1 Alert Status Timing Diagram