SNIS217C december 2020 – may 2023 TMP139
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Map
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YAH|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.4.6.1 ENEC CCC
The ENEC CCC is issued by the host controller to enable the event interrupt generation. The CCC takes effect after a Stop has been issued by the host controller. Once the ENEC is received, the TMP139 shall update the MR27 register bit IBI_ERROR_EN to 1'b1.
It is illegal for the host controller to send the ENINT bit as 0.
The command may be issued either as a broadcast command or as a direct command to TMP139 as shown in Figure 7-25 and Figure 7-26.
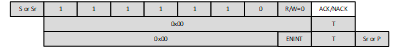 Figure 7-25 ENEC CCC Broadcast
Figure 7-25 ENEC CCC Broadcast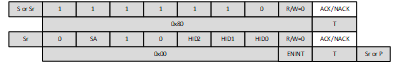 Figure 7-26 ENEC CCC Direct
Figure 7-26 ENEC CCC DirectThe command may be issued either as a broadcast or as a direct command, as shown in Figure 7-27 and Figure 7-28, with PEC Enabled. In such a case the host controller shall append the PEC byte calculated on all bytes except the byte with 7'h7E and R/W=0 after the Start or Repeated Start.
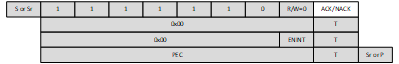 Figure 7-27 ENEC CCC Broadcast with PEC Enabled
Figure 7-27 ENEC CCC Broadcast with PEC Enabled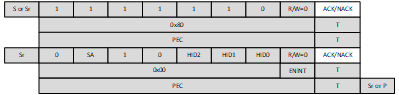 Figure 7-28 ENEC CCC Direct with PEC Enabled
Figure 7-28 ENEC CCC Direct with PEC EnabledTMP139 NACKs the ENEC CCC if the previous transaction has a parity or PEC error and the host starts the transaction with a Repeated Start.