SLVSGK4A November 2021 – June 2022 TPS22953-Q1 , TPS22954-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.3 Thermal Information
- 7.4 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics – VBIAS = 5 V
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics – VBIAS = 3.3 V
- 7.7 Electrical Characteristics – VBIAS = 2.5 V
- 7.8 Switching Characteristics – CT = 1000 pF
- 7.9 Switching Characteristics – CT = 0 pF
- 7.10 Typical DC Characteristics
- 7.11 Typical Switching Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 On and Off Control (EN Pin)
- 9.3.2 Voltage Monitoring (SNS Pin)
- 9.3.3 Power Good (PG Pin)
- 9.3.4 Supervisor Fault Detection and Automatic Restart
- 9.3.5 Manual Restart
- 9.3.6 Thermal Shutdown
- 9.3.7 Reverse Current Blocking (TPS22953-Q1 Only)
- 9.3.8 Quick Output Discharge (QOD) (TPS22954-Q1 Only)
- 9.3.9 VIN and VBIAS Voltage Range
- 9.3.10 Adjustable Rise Time (CT Pin)
- 9.3.11 Power Sequencing
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DQC|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DQC|10
Orderable Information
10.1.4 Monitoring a Downstream Voltage
The SNS pin can be used to monitor other system voltages in addition to VOUT. The status of the monitored voltage are indicated by the PG pin which can be pulled up to VOUT or another voltage. Figure 10-2 shows an example of the TPS2295x-Q1 monitoring the output of a downstream DC/DC regulator. In this case, the switch turns on when the power supply is above the UVLO, but the PG is not asserted until the DC/DC regulator has started up.
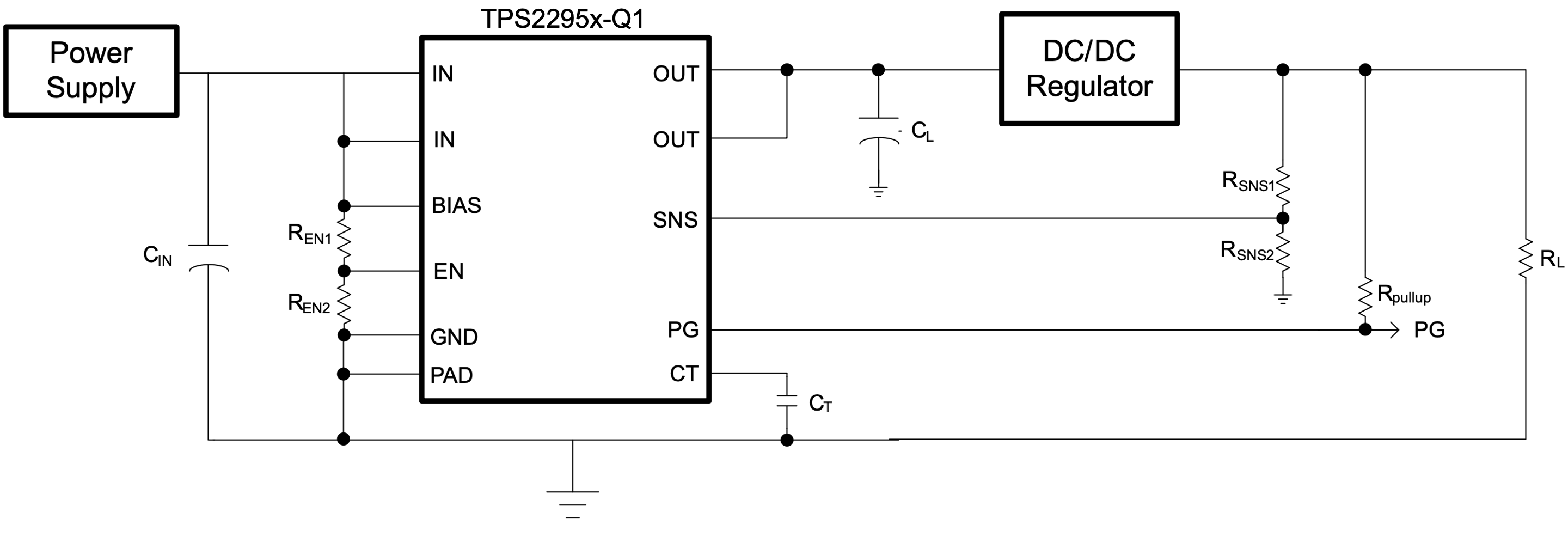 Figure 10-2 Monitoring a Downstream Voltage Schematic
Figure 10-2 Monitoring a Downstream Voltage SchematicIn this application, if the DC/DC Regulator is shut down, the supervisor registers this as a fault case and resets the load switch.