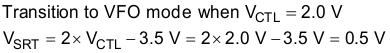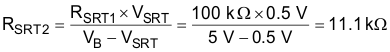SLVSB97E July 2012 – January 2018 TPS23751 , TPS23752
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 ESD Ratings: Surge
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Electric Characteristics - Controller Section
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics - Sleep Mode (TPS23752 Only)
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics - PoE Interface Section
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 PoE Overview
- 7.4.2
Sleep Mode Operation (TPS23752 only)
- 7.4.2.1 Converter Controller Features
- 7.4.2.2 PWM and VFO Operation; CTL, SRT, and SRD Pin Relationships to Output Load Current
- 7.4.2.3 Bootstrap Topology
- 7.4.2.4 Current Slope Compensation and Current Limit
- 7.4.2.5 RT
- 7.4.2.6 T2P, Startup and Power Management
- 7.4.2.7 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4.2.8 Adapter ORing
- 7.4.2.9 Using DEN to Disable PoE
- 7.4.2.10 ORing Challenges
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Input Bridges and Schottky Diodes
- 8.2.2.2 Protection, D1
- 8.2.2.3 Capacitor, C1
- 8.2.2.4 Detection Resistor, RDEN
- 8.2.2.5 Classification Resistor, RCLS
- 8.2.2.6 APD Pin Divider Network, RAPD1, RAPD2
- 8.2.2.7 Setting the PWM-VFO Threshold using the SRT pin
- 8.2.2.8 Setting Frequency (RT)
- 8.2.2.9 Current Slope Compensation
- 8.2.2.10 Voltage Feed-Forward Compensation
- 8.2.2.11 Estimating Bias Supply Requirements and Cvc
- 8.2.2.12 Switching Transformer Considerations and RVC
- 8.2.2.13 T2P Pin Interface
- 8.2.2.14 Softstart
- 8.2.2.15 Special Switching MOSFET Considerations
- 8.2.2.16 ESD
- 8.2.2.17 Thermal Considerations and OTSD
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Orderable Information
8.2.2.7 Setting the PWM-VFO Threshold using the SRT pin
The TPS23751 and TPS23752 internally compares modified voltages at the SRT and CTL pins to determine the operating mode. The designer should consider the light load operating point (considering the value of VCTL) where synchronous rectifier (M2 in Figure 31) gate drive and switching losses nearly match conduction losses of the rectifier diode (DOUT in Figure 31). Typically, the designer characterizes circuit efficiency, output load, and control pin (VCTL) voltage and then select the transition point. Both VFO → PWM (occurs at higher load current due to natural hysteresis) and PWM → VFO (occurs at slightly lower load current) transitions should be considered when choosing the VSRT setpoint. As an example:
- Assume that the desired efficiency transition threshold occurs at 18% of full load and VCTL = 2.0 V
- Determine where to set VSRT.
- Set VSRT using a voltage divider from VB to ARTN as shown in Figure 31.
- Choose RSRT1 = 100 kΩ and then calculate RSRT2 as follows:
- Select 11 kΩ for RSRT2.