SLVSDW2B December 2018 – November 2020 TPS23755
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 CLS Classification
- 7.3.2 DEN Detection and Enable
- 7.3.3 Internal Pass MOSFET
- 7.3.4
DC-DC Controller Features
- 7.3.4.1 VCC, VB and Advanced PWM Startup
- 7.3.4.2 CS, Current Slope Compensation and Blanking
- 7.3.4.3 COMP, FB, CP and Opto-less Feedback
- 7.3.4.4 FRS Frequency Setting and Synchronization
- 7.3.4.5 Frequency Dithering for Spread Spectrum Applications
- 7.3.4.6 SST and Soft-Start of the Switcher
- 7.3.4.7 AUX_V, AUX_D and Secondary Adapter Or'ing
- 7.3.5 Internal Switching FET - DRAIN, RSNS, SRF and SRR
- 7.3.6 VPD Supply Voltage
- 7.3.7 VDD Supply Voltage
- 7.3.8 GND
- 7.3.9 VSS
- 7.3.10 Exposed Thermal PAD
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Input Bridges and Schottky Diodes
- 8.2.2.2 Protection, D1
- 8.2.2.3 Capacitor, C1
- 8.2.2.4 Detection Resistor, RDEN
- 8.2.2.5 Classification Resistor, RCLS
- 8.2.2.6 Bulk Capacitance, CBULK
- 8.2.2.7 Output Voltage Feedback Divider, RAUX, R1,R2
- 8.2.2.8 Setting Frequency, RFRS
- 8.2.2.9 Frequency Dithering, RDTR and CDTR
- 8.2.2.10 Bias Voltage, CVB and DVB
- 8.2.2.11 Transformer design, T1
- 8.2.2.12 Current Sense Resistor, RCS
- 8.2.2.13 Current Slope Compensation, RS
- 8.2.2.14 Bias Supply Requirements, CCC, DCC
- 8.2.2.15 Switching Transformer Considerations, RVCC and CCC2
- 8.2.2.16 Primary FET Clamping, RCL, CCL, and DCL
- 8.2.2.17 Converter Output Capacitance, COUT
- 8.2.2.18 Secondary Output Diode Rectifier, DOUT
- 8.2.2.19 Slew rate control, RSRF and RSRR
- 8.2.2.20 Shutdown at Low Temperatures, DVDD and CVDD
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RJJ|23
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
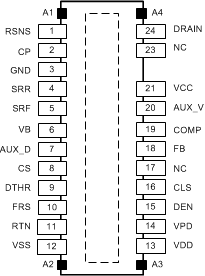 Figure 5-1 RJJ Package24-Pin VSONTop View
Figure 5-1 RJJ Package24-Pin VSONTop ViewTable 5-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO. | NAME | ||
| 1 | RSNS | O | Switching Power FET source connection. Connect to the external power current sense resistor. |
| 2 | CP | O | CP provides the clamp for the primary side regulation loop. Connect this pin to the lower end of the second primary side winding of the transformer. |
| 3 | GND | — | Power ground used by the flyback power FET gate driver and CP. Connect to RTN. |
| 4 | SRR | I | Switching FET Gate sinking current input, used for EMI control. Connect a resistance from SRR to GND to control the Vds rate of rise. |
| 5 | SRF | I | Switching FET Gate sourcing current input, used for EMI control. Connect a resistance from SRF to VB to control the Vds rate of fall. |
| 6 | VB | O | 5-V bias rail for the switching FET gate driver circuit. For internal use only. Bypass with a 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor and 6.2-V Zener diode to GND pin. |
| 7 | AUX_D | I | Auxiliary supply detect, internally pulled-up to approximately 5 V. Pull this pin low, typically through an optocoupler from the secondary side, to step down the output voltage of the DC-DC converter when a secondary side auxiliary supply is connected. |
| 8 | CS | I | DC-DC controller current sense input. Connect directly to the external power current sense resistor. |
| 9 | DTHR | O | Used for spread spectrum frequency dithering. Connect a capacitor from DTHR to RTN and a resistor from DTHR to FRS. If dithering is not used, short DTHR to VB pin. |
| 10 | FRS | I/O | This pin controls the switching frequency of the DC-DC converter. Tie a resistor from this pin to RTN to set the frequency. |
| 11 | RTN | — | RTN is the output of the PoE hotswap and the reference ground for the DC-DC controller. |
| 12 | VSS | — | Negative power rail derived from the PoE source. |
| 13 | VDD | — | Source of DC-DC converter start-up current. Connect to VPD for most applications. |
| 14 | VPD | — | Positive input power rail for PoE interface circuit. Derived from the PoE source. Bypass with a 0.1 µF to VSS and protect with a TVS. |
| 15 | DEN | I/O | Connect a 24.9-kΩ resistor from DEN to VPD to provide the PoE detection signature. Pulling this pin to VSS during powered operation causes the internal hotswap MOSFET to turn off. |
| 16 | CLS | O | Connect a resistor from CLS to VSS to program the classification current. |
| 17 | NC | — | No connect pin. Leave open. |
| 18 | FB | I | Converter error amplifier inverting (feedback) input. It is typically driven by a voltage divider from the auxiliary winding. Also connect to the COMP compensation network. |
| 19 | COMP | O | Compensation output of the DC-DC convertor error amplifier. Connect the compensation networks from this pin to the FB pin to compensate the converter. |
| 20 | AUX_V | O | AUX_V works with AUX_D to step down the output voltage setting of the DC-DC converter when an auxiliary supply is detected. Typically connected to FB pin through a resistor which defines the new voltage setting. |
| 21 | VCC | I/O | DC/DC converter bias voltage. The internal startup current source and converter bias winding output power this pin. Connect a 1-µF minimum ceramic capacitor to RTN. |
| 23 | NC | — | No connect pin. Leave open. |
| 24 | DRAIN | O | Drain connection to the internal switching power MOSFET of the DC/DC controller. |
| - | PAD | — | The exposed thermal pad must be connected to VSS. A large fill area is required to assist in heat dissipation. |
| A1-A4 | ANCHORS | — | Should be soldered to PCB for mechanical performance. These pins are not connected internally. |