SLVSET8A May 2019 – August 2019 TPS2596
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Precision Current Limiting and Protection for White Goods
- 9.2.2 Design Requirements
- 9.2.3 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.4 Support Component Selection: RFLT and CIN
- 9.2.5 Application Curves
- 9.3 System Examples
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Orderable Information
9.3.2 Precision Current Limiting and Protection in Appliances
Household and similar electrical appliances are subjected to various tests (for example: needle flame, glow wire) as part of the certification for electrical and fire safety compliance as per the regulations. Special precautions need to be taken in the design to pass these tests, which include the use of higher grade flame retardant plastic material for the housing enclosures. There are certain provisions in the standard which can be leveraged to make the certification easier, faster and also reduce the cost of plastic materials. For example, any node which has less than 15 W of power available to it is classified as a LPC (Low Power Circuit as per the definition in IEC 60335-1) and deemed to be safe. All circuits or sub-systems further downstream from a LPC node are exempt from the aforementioned tests.
eFuses like TPS2596xx are a simple and cost effective way to limit the power delivered to the downstream load. The key parameter to be considered is the current imit tolerance and accuracy, which determines how high one can set the nominal current limit without exceeding the 15-W power limit on the upper end. On the lower end, it determines the maximum power the load can draw in normal conditions without hitting the current limit. TPS2596xx provides a current limit accuracy of ±5 % (at room temperature), which allows the load to use nearly 90% out of the 15-W limit under normal operating conditions.
In contrast, an alternative current limiting solution with wider current limit tolerance, say ±25 % would leave only 50 % out of 15 W for the load circuit to operate under normal conditions. This places severe constraints on the load circuit design and/or capabilities.
Figure 61 shows a sub-system example of a refrigerator and freezer system where TPS2596xx is used for precision current limiting and protection of 15-W rails to ease the qualification as low-power circuit as per IEC 60335-1.
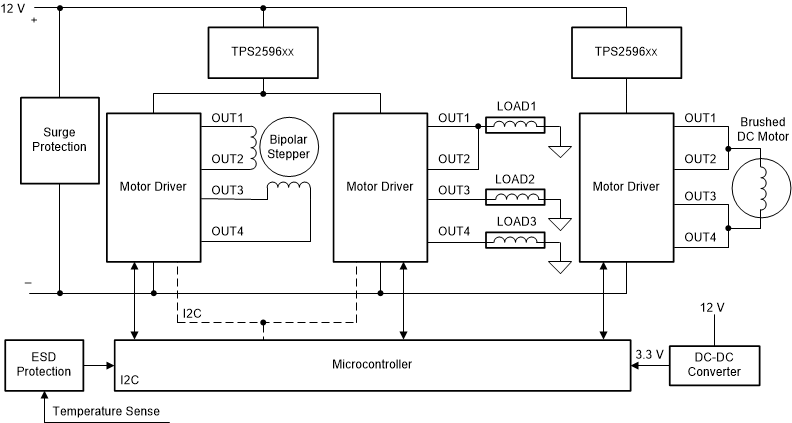 Figure 61. Appliances 15-W LPC Implementation Example
Figure 61. Appliances 15-W LPC Implementation Example TIDA-010004 demonstrates a multi-load drive using single driver chip with eFuse for protection and 15-W LPC implementation.
Refer to this Designing Low-Power Circuits (LPCs) using TPS2596 for Household and similar Appliances application note for a detailed insight into implementing power limited circuits using eFuses.