SLVSFJ6 November 2020 TPS27SA08
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Summary Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Protection Mechanisms
- 9.3.2 Diagnostic Mechanisms
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Orderable Information
9.3.1.6 Fault Event – Timing Diagrams
All timing diagrams assume that the SELx pins are set to 00.
The LATCH, DIA_EN, and EN pins are controlled by the user. The timing diagrams represent a possible use-case.
Figure 9-4 shows the active current limiting behavior of TPS27SA08 device and the LATCH pin functionality. The switch will not shutdown until either the energy limit or the thermal shutdown is reached.
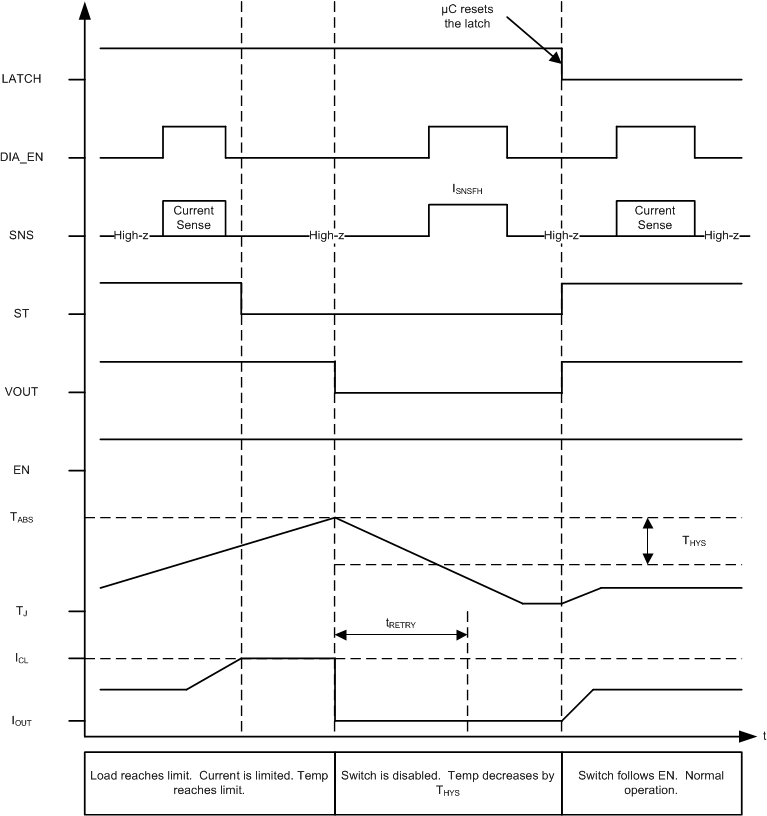 Figure 9-4 Current Limit - Latched Behavior
Figure 9-4 Current Limit - Latched Behavior Figure 9-5 shows the active current limiting behavior of TPS27SA08 device. The switch will not shutdown until either thermal shutdown or energy limit is tripped. In this example, LATCH is tied to GND and the switch is turned ON when the FET temperature is low enough.
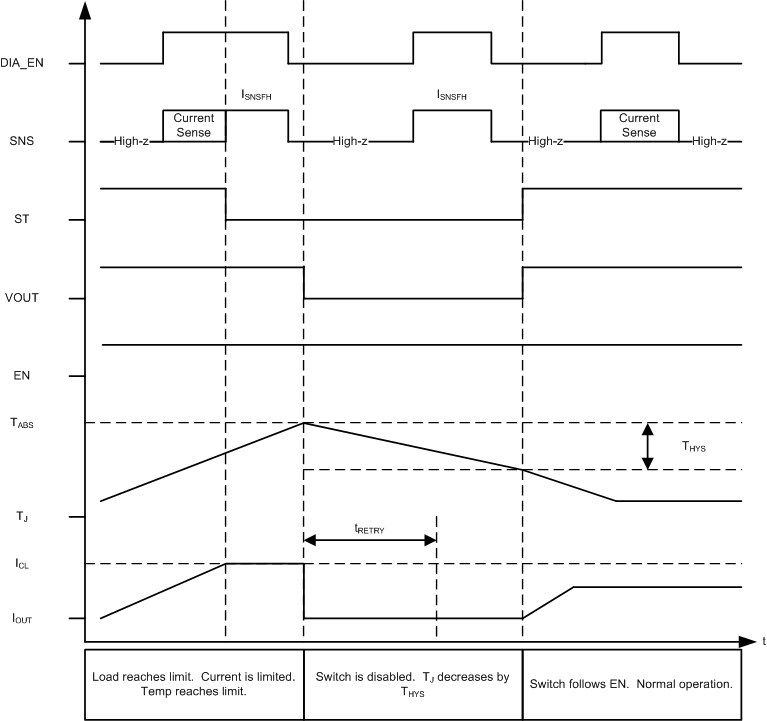 Figure 9-5 Current Limit - LATCH Pin
Permanently Low
Figure 9-5 Current Limit - LATCH Pin
Permanently LowdeWhen the switch retries after a shutdown event, the SNS fault indication will remain until VOUT has risen to VBB – 1.8 V. Once VOUT has risen, the SNS fault indication is reset and current sensing is available. ST fault indication is reset as soon as the switch is re-enabled (does not wait for VOUT to rise). If there is a short-to-ground and VOUT is not able to rise, the SNS fault indication will remain indefinitely. The following diagram illustrates auto-retry behavior and provides a zoomed-in view of the fault indication during retry.
Figure 9-6 assumes that tRETRY has expired by the time that TJ reaches the hysteresis threshold.
LATCH = 0 V and DIA_EN = 5 V
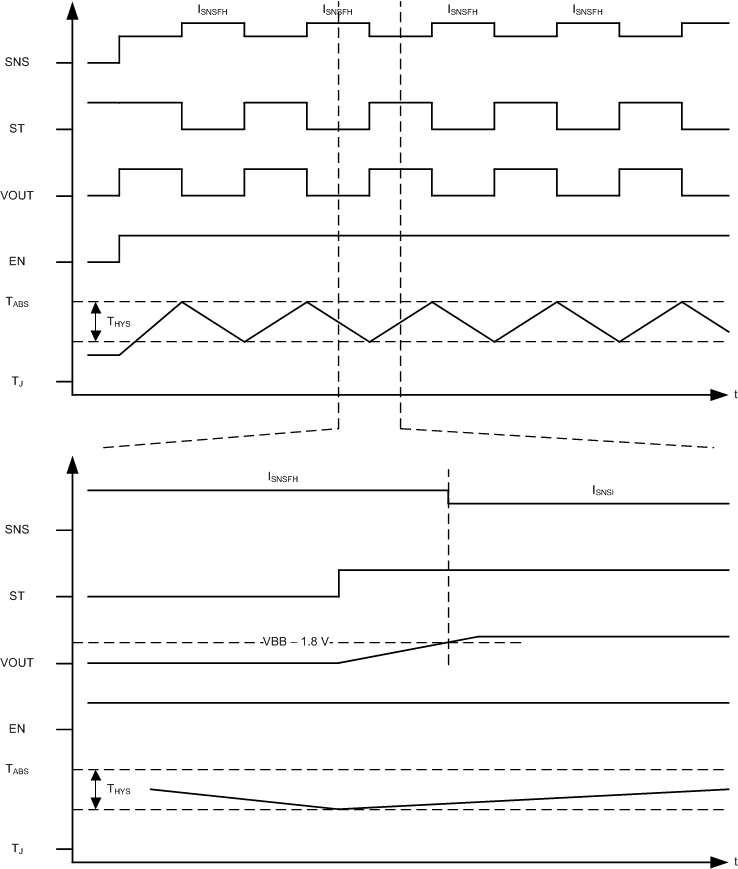 Figure 9-6 Fault Indication During Retry
Figure 9-6 Fault Indication During Retry