SLUS719H MARCH 2007 – May 2019 TPS40192 , TPS40193
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.3 Output Capacitor Selection (C8)
- 8.2.2.4 Peak Current Rating of the Inductor
- 8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor Selection (C7)
- 8.2.2.6 MOSFET Switch Selection (Q1, Q2)
- 8.2.2.7 Boot Strap Capacitor
- 8.2.2.8 Input Bypass Capacitor (C6)
- 8.2.2.9 BP5 Bypass Capacitor (C5)
- 8.2.2.10 Input Voltage Filter Resistor (R11)
- 8.2.2.11 Short Circuit Protection (R9)
- 8.2.2.12 Feedback Compensation (Modeling the Power Stage)
- 8.2.2.13 Feedback Divider (R7, R8)
- 8.2.2.14 Error Amplifier Compensation (R6, R10, C1, C2, C3)
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Orderable Information
8.2.2.6 MOSFET Switch Selection (Q1, Q2)
The switching losses for the high-side MOSFET are estimated by Equation 17.
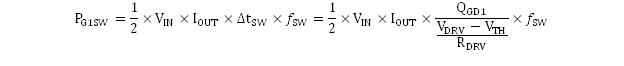
Switching losses in this design are highest at high-line. Designing for 1 W of total loss in each MOSFET and 60% of the total high-side MOSFET losses in switching losses, estimate the maximum gate-drain charge for the design by using Equation 18.
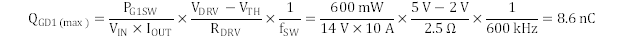
The switching losses of the synchronous rectifier are lower than the switching losses of the main MOSFET because the voltage across the MOSFET at the point of switching is reduced to the forward voltage drop across the body diode of the SR MOSFET and are estimated by using Equation 19. The conduction losses in the main MOSFET are estimated by the RMS current through the MOSFET times its RDS(on).
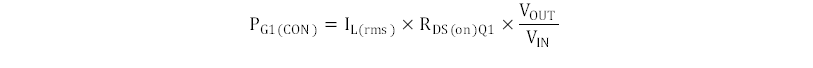
Estimating about 40% of total MOSFET losses to be high-side conduction losses, the maximum RDS(on) of the high-side MOSFET can be estimated by using Equation 20.
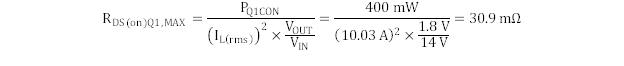
Estimating 80% of total low-side MOSFET losses in conduction losses, repeat the calculation for the synchronous rectifier, whose losses are dominated by the conduction losses. Calculate the maximum RDS(on) of the synchronous rectifier by Equation 21.
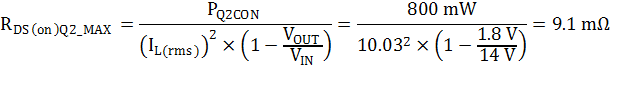
Table 4. Power MOSFET Requirements
| PARAMETER | SYMBOL | VALUE | UNITS |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-side MOSFET on-resistance | RDS(on)Q1 | 30.9 | mΩ |
| High-side MOSFET gate-to-drain charge | QGD1 | 8.5 | nC |
| Low-side MOSFET on-resistance | RDS(on)Q2 | 8.8 | mΩ |
The IRF7466 has an RDS(on)MAX of 30.9 mΩ at 4.5-V gate drive and only 8.0-nC VGD "Miller" charge with a 4.5-V gate drive, and is chosen as a high-side MOSFET. The IRF7834 has an RDS(on)Q1,MAX of 5.5 mΩ at 4.5-V gate drive and 44 nC of total gate charge. These two FETs have maximum total gate charges of 23 nC and 44 nC respectively, which draws 40.2-mA from the 5-V regulator, less than its 50-mA minimum rating.