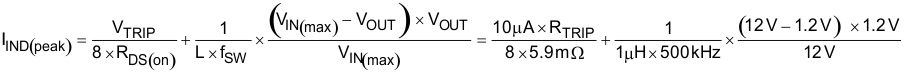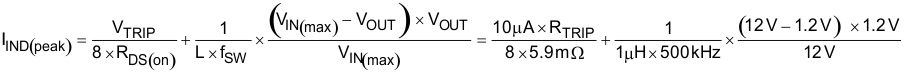SLUSBP9C SEPTEMBER 2013 – June 2018 TPS53513
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 5-V LDO and VREG Start-Up
- 7.3.2 Enable, Soft Start, and Mode Selection
- 7.3.3 Frequency Selection
- 7.3.4 D-CAP3 Control and Mode Selection
- 7.3.5 Power-Good
- 7.3.6 Current Sense and Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.7 Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
- 7.3.8 Out-Of-Bounds Operation
- 7.3.9 UVLO Protection
- 7.3.10 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RVE|28
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RVE|28
Orderable Information
8.2.2.3 Choose the Inductor
Determine the inductance value to set the ripple current at approximately ¼ to ½ of the maximum output current. Larger ripple current increases output ripple voltage, improves signal-to-noise ratio, and helps to stabilize operation.
Equation 7. 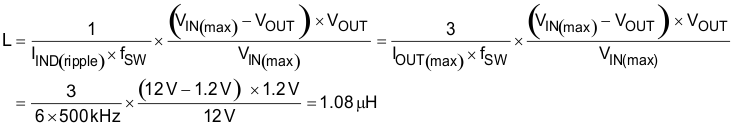

The inductor requires a low DCR to achieve good efficiency. The inductor also requires enough room above peak inductor current before saturation. The peak inductor current is estimated using Equation 8.
Equation 8.