SLVSGA9A March 2022 – August 2022 TPS55289
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 VCC Power Supply
- 7.3.2 EXTVCC Power Supply
- 7.3.3 Operation Mode Setting
- 7.3.4 Input Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.5 Enable and Programmable UVLO
- 7.3.6 Soft Start
- 7.3.7 Shutdown and Load Discharge
- 7.3.8 Switching Frequency
- 7.3.9 Switching Frequency Dithering
- 7.3.10 Inductor Current Limit
- 7.3.11 Internal Charge Path
- 7.3.12 Output Voltage Setting
- 7.3.13 Output Current Monitoring and Cable Voltage Droop Compensation
- 7.3.14 Output Current Limit
- 7.3.15 Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.16 Output Short Circuit Protection
- 7.3.17 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 REF Register (Address = 0h, 1h)
- 7.6.2 IOUT_LIMIT Register (Address = 2h) [reset = 11100100h]
- 7.6.3 VOUT_SR Register (Address = 3h) [reset = 00000001h]
- 7.6.4 VOUT_FS Register (Address = 4h) [reset = 00000011h]
- 7.6.5 CDC Register (Address = 5h) [reset = 11100000h]
- 7.6.6 MODE Register (Address = 6h) [reset = 00100000h]
- 7.6.7 STATUS Register (Address = 7h) [reset = 00000011h]
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RYQ|21
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.9 Switching Frequency Dithering
The TPS55289 provides an optional switching frequency dithering that is enabled by connecting a capacitor from the DITH/SYNC pin to ground. Figure 7-4 illustrates the dithering circuit. By charging and discharging the capacitor, a triangular waveform centered at 1 V is generated at the DITH/SYNC pin. The triangular waveform modulates the oscillator frequency by ±7% of the nominal frequency set by the resistance at the FSW pin. The capacitance at the DITH/SYNC pin sets the modulation frequency. A small capacitance modulates the oscillator frequency at a faster rate than a large capacitance. For the dithering circuit to effectively reduce peak EMI, the modulation rate normally is below 1 kHz. Equation 4 calculates the capacitance required to set the modulation frequency, FMOD.
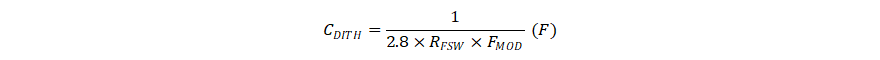
where
- RFSW is the switching frequency setting resistance (Ω) at the FSW pin.
- FMOD is the modulation frequency (Hz) of the dithering.
Connecting the DITH/SYNC pin below 0.4 V or above 1.2 V disables switching frequency dithering. The dithering function also is disabled when an external synchronous clock is used.
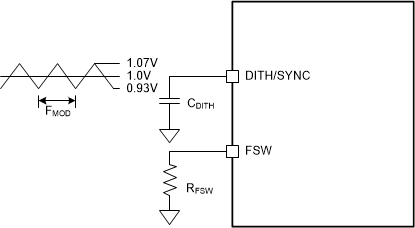 Figure 7-4 Switching Frequency Dithering
Figure 7-4 Switching Frequency Dithering