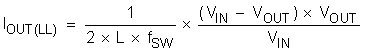SLUSED6 October 2020 TPS562202S
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRL|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.2 ECO Mode Control
The TPS562202S is designed with advanced Eco-mode to maintain high light load efficiency. As the output current decreases from heavy load condition, the inductor current is also reduced and eventually comes to point that its rippled valley touches zero level, which is the boundary between continuous conduction and discontinuous conduction modes. The rectifying MOSFET is turned off when the zero inductor current is detected. As the load current further decreases, the converter runs into discontinuous conduction mode. The on-time is kept almost the same as it was in continuous conduction mode so it takes more time to discharge the output capacitor with smaller load current to the level of the reference voltage. This makes the switching frequency lower, proportional to the load current, and keeps the light load efficiency high. The transition point to the light load operation IOUT(LL) current can be calculated in Equation 1.