SLUSDL0A January 2020 – March 2020 TPS59603-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DSG|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DSG|8
Orderable Information
7.3.4 Adaptive Dead-Time Control and Shoot-Through Protection
The driver utilizes an anti-shoot-through and adaptive dead-time control to minimize low-side body diode conduction time and maintain high efficiency. When the PWM input voltage becomes high, the low-side MOSFET gate voltage begins to fall after a propagation delay. At the same time, DRVL voltage is sensed, and high-side driving voltage starts to increase after DRVL voltage is lower than a proper threshold.
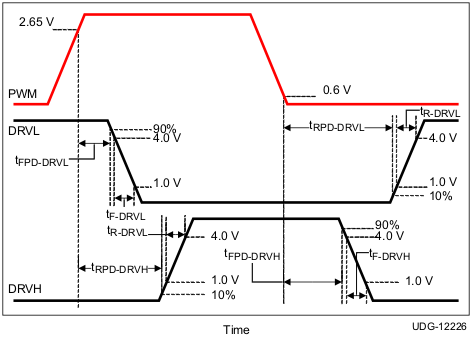 Figure 15. Rise and Fall Timing and Propagation Delay Definitions
Figure 15. Rise and Fall Timing and Propagation Delay Definitions Typical operation manages to near zero the dead-time between the low-side gate turn-off to high-side gate voltage turn-on, and high-side gate turn-off to low-side gate turn-on, in order to avoid simultaneous conduction of both MOSFETs, as well as to reduce body diode conduction and recovery losses. This operation also reduces ringing on the leading edge of the SW waveform.
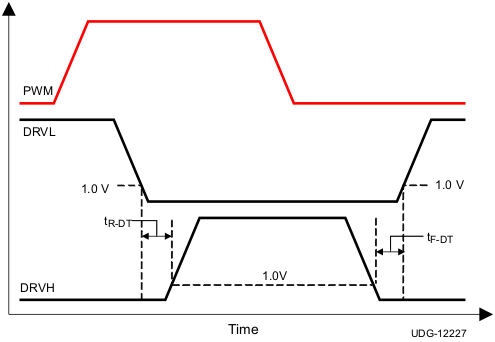 Figure 16. Dead-Time Definitions
Figure 16. Dead-Time Definitions