SLVS873F June 2015 – September 2021 TPS61098 , TPS610981 , TPS610982 , TPS610985 , TPS610986 , TPS610987
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Applications and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DSE|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.4.1.2 Low Power Mode
The TPS61098x works in Low Power mode when MODE pin is logic low. In Low Power mode, the LDO/load switch is turned off, so the peripherals can be disconnected to minimize the battery drain. The VSUB pin either outputs high impedance or is pulled to ground by internal active discharge circuit, depending on different versions. The boost converter consumes only 300 nA quiescent current typically, and can achieve up to 88% efficiency at 10 µA load.
The Low Power mode is designed to keep the load device powered with minimum power consumption. For example, it can be used to keep powering the main system, like an MCU, in a system's sleep mode even under < 0.7 V input voltage condition.
Figure 8-3 and Figure 8-4 illustrate the outputs of the TPS61098 and TPS610981 under different input voltages in Active mode and Low Power mode.
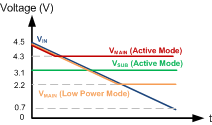 Figure 8-3 TPS61098 Output under Different Input Voltages
Figure 8-3 TPS61098 Output under Different Input Voltages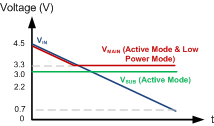 Figure 8-4 TPS610981 Output under Different Input Voltages
Figure 8-4 TPS610981 Output under Different Input VoltagesThe TPS610982 is an exception. Its LDO is always on in both Active mode and Low Power mode with higher quiescent current consumption than other versions. The TPS610982 can be used to replace discrete boost and LDO solutions where the LDO output is always on, and its two modes provide users two options of different quiescent current consumption and performance. Refer to Section 8.4.1, Section 7 and Section 7.6 for details.