SLVSAX2B September 2011 – June 2020 TPS61170-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRV|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRV|6
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.3 Switch Duty Cycle
The maximum switch duty cycle (D) of the TPS61170-Q1 is 90% (minimum). The duty cycle of a boost converter under continuous conduction mode (CCM) is given by:
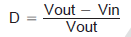
For a 5-V to 12-V application, the duty cycle is 58.3%, and for a 5-V to 24-V application, the duty cycle is 79.2%. The duty cycle must be lower than the maximum specification of 90% in the application; otherwise, the output voltage cannot be regulated.
Once the PWM switch is turned on, the TPS61170-Q1 device has minimum ON pulse width. This sets the limit of the minimum duty cycle. When operating at low duty cycles, the TPS61170-Q1 enters pulse-skipping mode. In this mode, the device turns the power switch off for several switching cycles to prevent the output voltage from rising above regulation. This operation typically occurs in light load condition when the PWM operates in discontinuous mode. See the Figure 10.