SLVSAJ0F November 2011 – October 2021 TPS62140 , TPS62140A , TPS62141 , TPS62142 , TPS62143
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGT|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGT|16
Orderable Information
9.2.2.2.1 Inductor Selection
The inductor selection is affected by several effects like inductor ripple current, output ripple voltage, PWM-to-PSM transition point, and efficiency. In addition, the inductor selected must be rated for appropriate saturation current and DC resistance (DCR). Equation 7 and Equation 8 calculate the maximum inductor current under static load conditions.
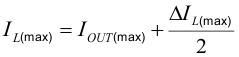
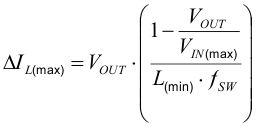
where
- IL(max) is the maximum inductor current
- ΔIL is the peak-to-peak inductor ripple current
- L(min) is the minimum effective inductor value
- fSW is the actual PWM switching frequency
Calculating the maximum inductor current using the actual operating conditions gives the minimum required inductor saturation current. It is recommended to add a margin of about 20%. A larger inductor value is also useful to get lower ripple current, but increases the transient response time and size as well. The following inductors have been used with the TPS6214x and are recommended for use:
| TYPE | INDUCTANCE (µH) | CURRENT (A)(1) | DIMENSIONS [L x B x H] (mm) | MANUFACTURER(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XFL4020-222ME_ | 2.2 µH, ±20% | 3.5 | 4 x 4 x 2.1 | Coilcraft |
| XFL4020-332ME_ | 3.3 µH, ±20% | 2.9 | 4 x 4 x 2.1 | Coilcraft |
| IHLP1212BZ-11 | 2.2 µH, ±20% | 3.0 | 3 x 3.6 x 2 | Vishay |
| IHLP1616AB-11 | 2.2 µH, ±20% | 2.75 | 4.05 x 4.45 x 1.2 | Vishay |
| DEM4518C 1235AS-H-3R3M | 3.3 µH, ±20% | 2.5 | 4.5 x 4.7 x 1.9 | Toko |
The inductor value also determines the load current at which the power-save mode is entered:
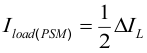
Using Equation 8, this current level can be adjusted by changing the inductor value.