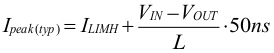SLUSDN9B November 2021 – July 2022 TPS62441-Q1 , TPS62442-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RQR|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RQR|14
Orderable Information
9.4.4 Current Limit and Short Circuit Protection
The TPS6244x-Q1 is protected against overload and short circuit events. The converter is not switching with the fixed frequency when in current limit. The converter resumes the fixed-frequency operation when the converter leaves current limit condition. If the inductor current exceeds the current limit, ILIMH, the high-side switch is turned off and the low-side switch is turned on to ramp down the inductor current. The high-side switch turns on again only if the current in the low-side switch has decreased below the low-side current limit, which can cause bursts or single pulses between the high-side and low-side current limit. Due to internal propagation delay, the actual current can exceed the static current limit. The dynamic current limit is given as:
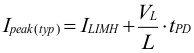
where
- ILIMH is the static current limit as specified in the electrical characteristics.
- L is the effective inductance at the peak current.
- VL is the voltage across the inductor (VIN – VOUT).
- tPD is the internal propagation delay of typically 50 ns.
The current limit can exceed static values, especially if the input voltage is high and very small inductances are used. The dynamic high-side switch peak current can be calculated as follows: