SLVSA92C November 2011 – September 2020 TPS63060 , TPS63061
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DSC|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DSC|10
Orderable Information
8.4.6 Dynamic Current Limit
The dynamic current limit function maintains the output voltage regulation when the power source becomes weaker. The maximum current allowed through the switch depends on the voltage applied at the input terminal of the TPS6306x devices. Figure 8-5 shows this dependency, and the ISW vs VIN. The dynamic current limit has its lowest value when reaching the minimum recommended supply voltage at VIN.
Given the ISW value from Figure 8-5, is then possible to calculate the output current reached in boost mode using Equation 1 and Equation 2 and in buck mode using Equation 3 and Equation 4.
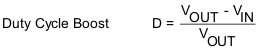

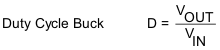
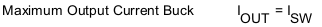
where
- η is the estimated converter efficiency (use the number from the efficiency curves or 0.80 as an assumption)
- f is the converter switching frequency (typical 2.4 MHz)
- L is the selected inductor value
If the die temperature increases above the recommended maximum temperature, the dynamic current limit becomes active. The current limit is reduced with temperature increasing.
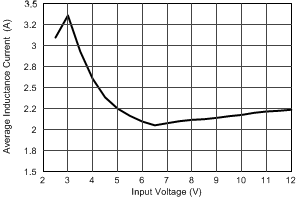 Figure 8-5 Average Inductance Current vs Input Voltage
Figure 8-5 Average Inductance Current vs Input Voltage