SBVS387C February 2020 – January 2022 TPS784-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2 Typical Application
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRB|8
Orderable Information
10.1.1 Additional Layout Considerations
The high impedance of the FB pin makes the regulator sensitive to parasitic capacitances that may couple undesirable signals from nearby components (especially from logic and digital devices, such as microcontrollers and microprocessors); these capacitively-coupled signals may produce undesirable output voltage transients. In these cases, TI recommends using a fixed-voltage version of the device, or isolating the FB node by placing a copper ground plane on the layer directly underneath the LDO circuitry and FB pin to minimize any undesirable signal coupling.
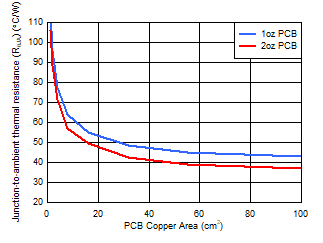
| 4-layer PCB |
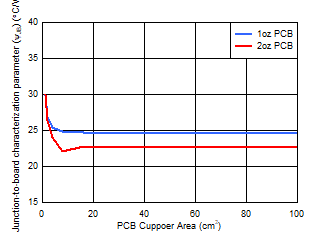
| 4-layer PCB |
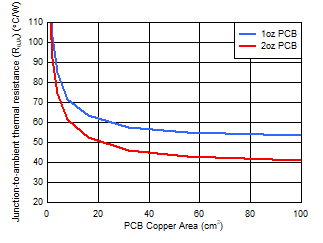
| 2-layer PCB |
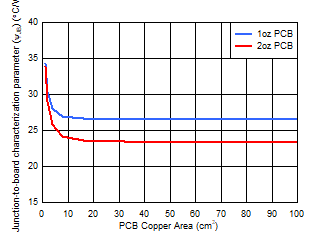
| 2-layer PCB |