SLUSDC0C October 2018 – November 2021 UCC21530
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Power Ratings
- 6.6 Insulation Specifications
- 6.7 Safety-Related Certifications
- 6.8 Safety-Limiting Values
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics
- 6.11 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DWK|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11.2 Layout Example
Figure 11-1shows a 2-layer PCB layout example with the signals and key components labeled.
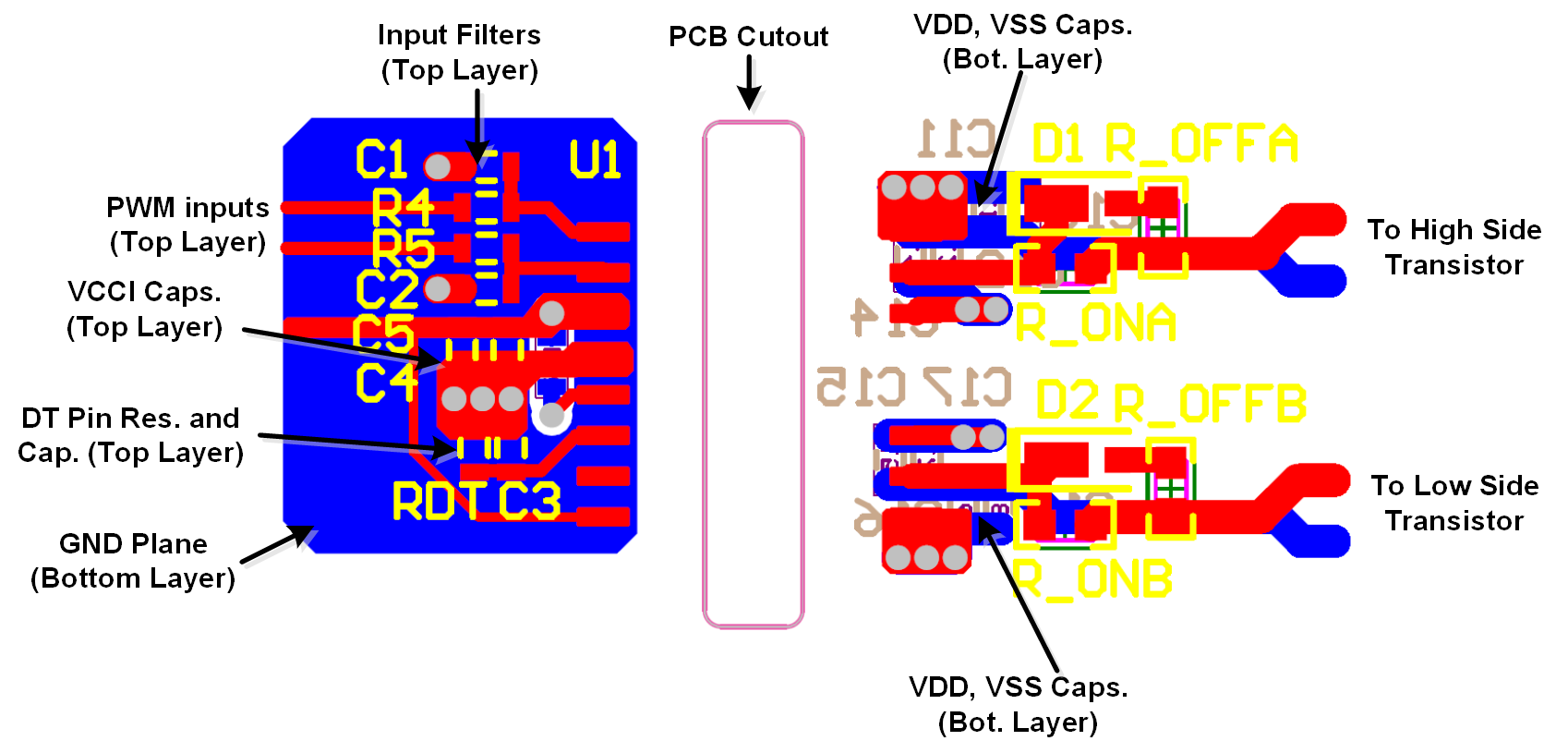 Figure 11-1 Layout Example
Figure 11-1 Layout ExampleFigure 11-2 and Figure 11-3 shows top and bottom layer traces and copper.
There are no PCB traces or copper between the primary and secondary side, which ensures isolation performance.
PCB traces between the high-side and low-side gate drivers in the output stage are increased to maximize the creepage distance for high-voltage operation, which will also minimize cross-talk between the switching node VSSA (SW), where high dv/dt may exist, and the low-side gate drive due to the parasitic capacitance coupling.
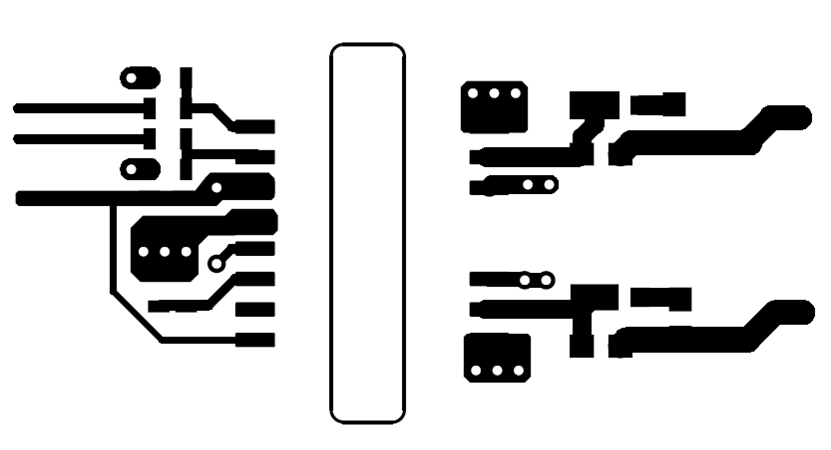 Figure 11-2 Top
Layer Traces and Copper
Figure 11-2 Top
Layer Traces and Copper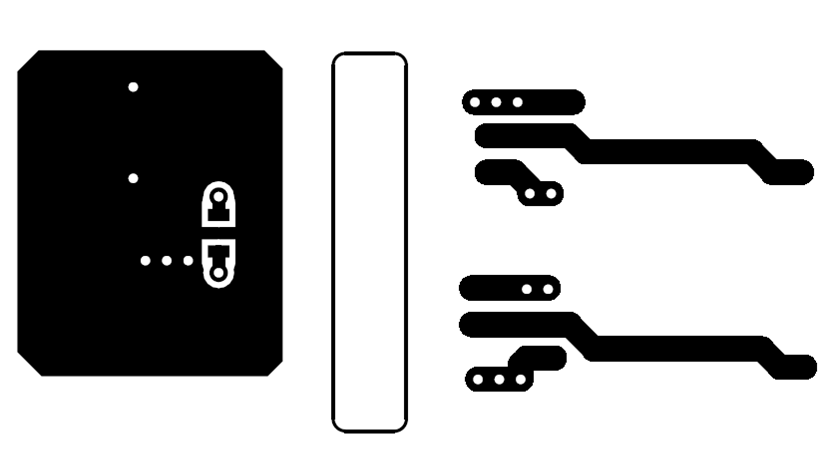 Figure 11-3 Bottom Layer Traces and Copper
Figure 11-3 Bottom Layer Traces and CopperFigure 11-4 and Figure 11-5 are 3D layout pictures with top view and bottom views.
The location of the PCB cutout between the primary side and secondary sides, which ensures isolation performance.
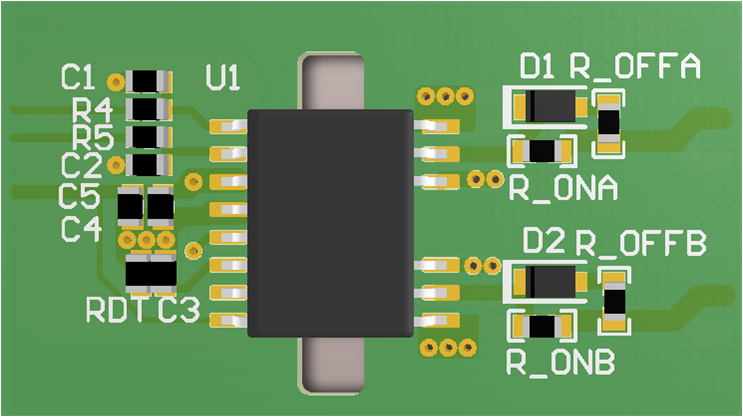 Figure 11-4 3-D
PCB Top View
Figure 11-4 3-D
PCB Top View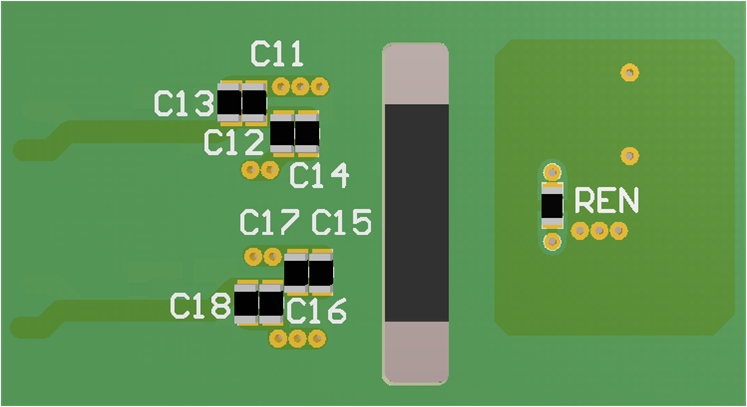 Figure 11-5 3-D
PCB Bottom View
Figure 11-5 3-D
PCB Bottom View