JAJSEG4C December 2013 – July 2018
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Details of a Qi Wireless Power System and bq51003 Power Transfer Flow Diagrams
- 8.3.2 Dynamic Rectifier Control
- 8.3.3 Dynamic Efficiency Scaling
- 8.3.4 RILIM Calculations
- 8.3.5 Input Overvoltage
- 8.3.6 Adapter Enable Functionality and EN1/EN2 Control
- 8.3.7 End Power Transfer Packet (WPC Header 0x02)
- 8.3.8 Status Outputs
- 8.3.9 WPC Communication Scheme
- 8.3.10 Communication Modulator
- 8.3.11 Adaptive Communication Limit
- 8.3.12 Synchronous Rectification
- 8.3.13 Temperature Sense Resistor Network (TS)
- 8.3.14 3-State Driver Recommendations for the TS-CTRL Pin
- 8.3.15 Thermal Protection
- 8.3.16 WPC v1.2 Compliance – Foreign Object Detection
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
7.6 Typical Characteristics
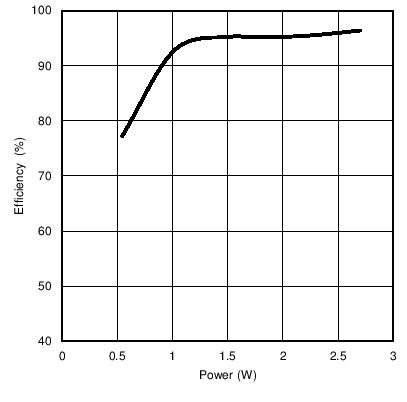 Figure 1. Rectifier Efficiency
Figure 1. Rectifier Efficiency 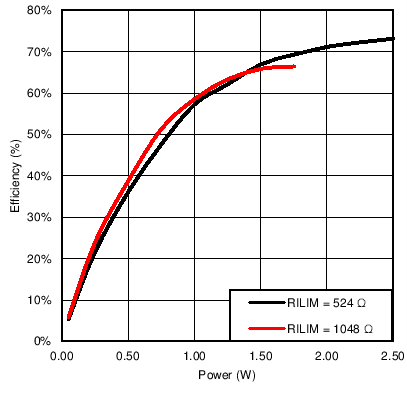 Figure 3. Light Load System Efficiency Improvement Due to Dynamic Efficiency Scaling Feature
Figure 3. Light Load System Efficiency Improvement Due to Dynamic Efficiency Scaling Feature 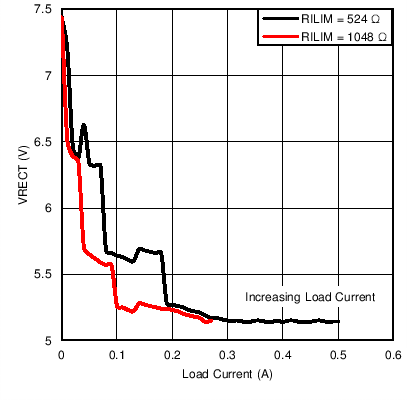 Figure 5. VRECT vs ILOAD at RILIM = 524 Ω and 1048 Ω
Figure 5. VRECT vs ILOAD at RILIM = 524 Ω and 1048 Ω 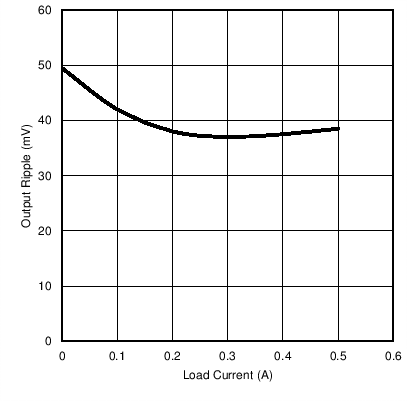 Figure 7. Output Ripple vs ILOAD (COUT = 1 µF) Without Communication
Figure 7. Output Ripple vs ILOAD (COUT = 1 µF) Without Communication 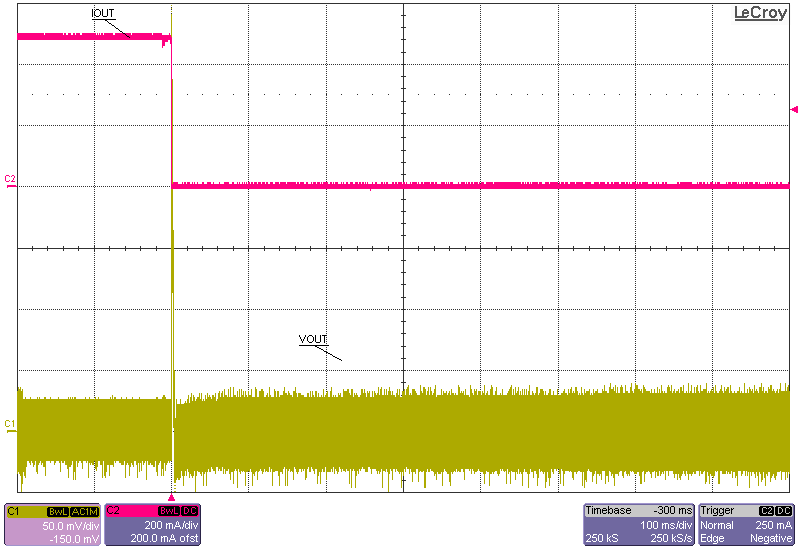 Figure 9. 0.5-A Instantaneous Load Dump
Figure 9. 0.5-A Instantaneous Load Dump 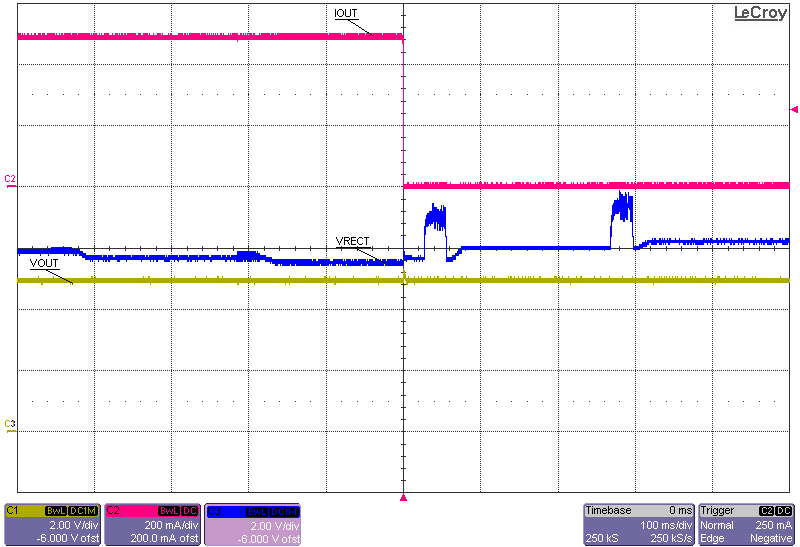 Figure 11. 0.5-A Load Dump Full System Response
Figure 11. 0.5-A Load Dump Full System Response 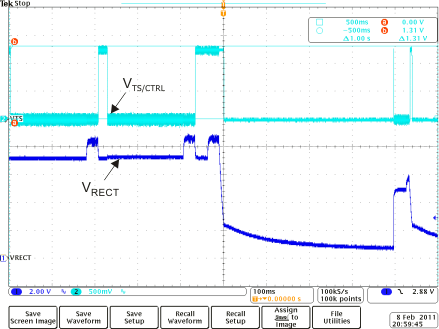 Figure 13. TS Fault
Figure 13. TS Fault 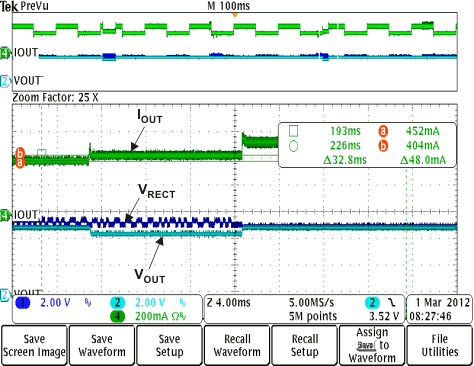 Figure 15. Adaptive Communication Limit Event Where the Current Limit is IOUT + 50 mA (IOUT-DC > 300 mA)
Figure 15. Adaptive Communication Limit Event Where the Current Limit is IOUT + 50 mA (IOUT-DC > 300 mA) 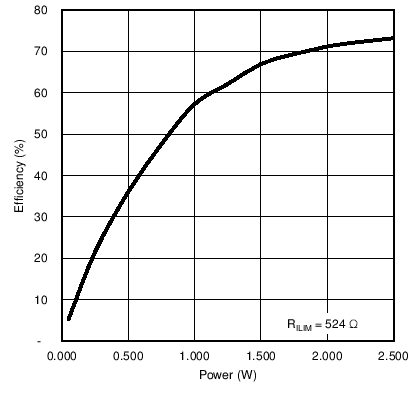 Figure 2. System Efficiency from DC Input to DC Output
Figure 2. System Efficiency from DC Input to DC Output 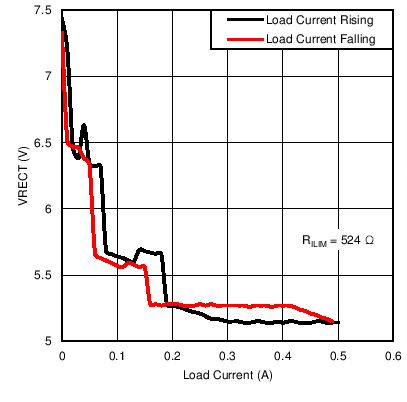 Figure 4. VRECT vs ILOAD at RILIM = 524 Ω
Figure 4. VRECT vs ILOAD at RILIM = 524 Ω 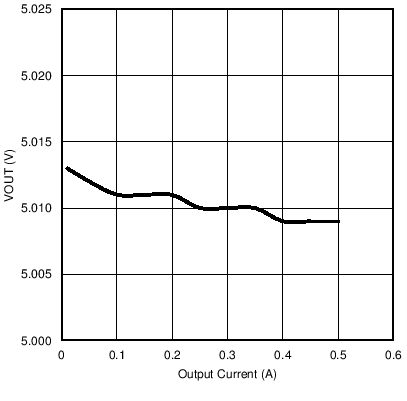 Figure 6. ILOAD Sweep (I-V Curve)
Figure 6. ILOAD Sweep (I-V Curve) 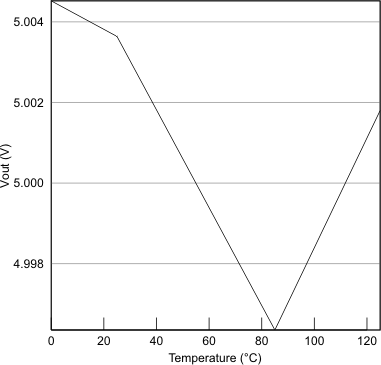 Figure 8. VOUT vs Temperature
Figure 8. VOUT vs Temperature 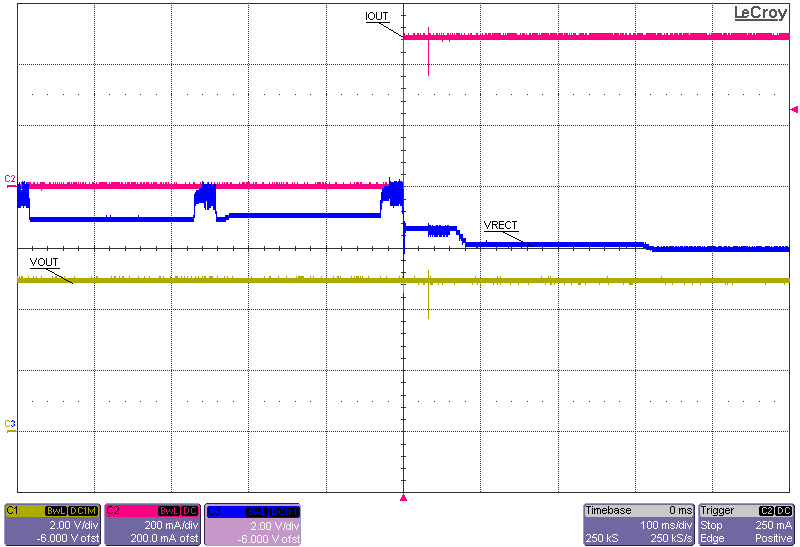 Figure 10. 0.5-A Load Step Full System Response
Figure 10. 0.5-A Load Step Full System Response 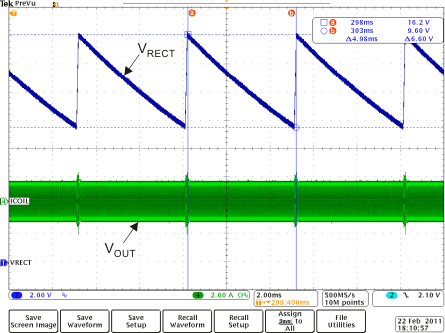 Figure 12. Rectifier Overvoltage Clamp (fop = 110 kHz)
Figure 12. Rectifier Overvoltage Clamp (fop = 110 kHz) 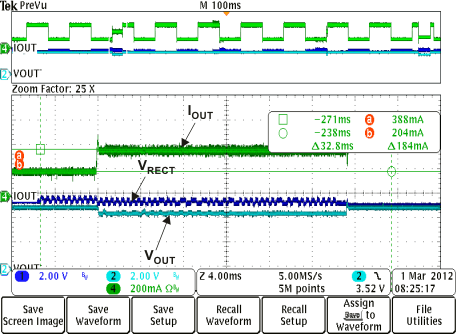 Figure 14. Adaptive Communication Limit Event Where the 400-mA Current Limit is Enabled (IOUT-DC < 300 mA)
Figure 14. Adaptive Communication Limit Event Where the 400-mA Current Limit is Enabled (IOUT-DC < 300 mA) 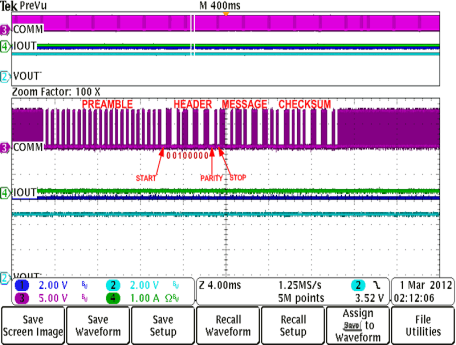 Figure 16. Rx Communication Packet Structure
Figure 16. Rx Communication Packet Structure