JAJSFB9A April 2018 – February 2019 DRV5056
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
8.1.4 Designing for Wire Break Detection
Some systems must detect if interconnect wires become open or shorted. The DRV5056 can support this function.
First, select a sensitivity option that causes the output voltage to stay within the VL range during normal operation. Second, add a pullup resistor between OUT and VCC. TI recommends a value between 20 kΩ to 100 kΩ, and the current through OUT must not exceed the IO specification, including current going into an external ADC. Then, if the output voltage is ever measured to be within 150 mV of VCC or GND, a fault condition exists. Figure 19 shows the circuit, and Table 1 describes fault scenarios.
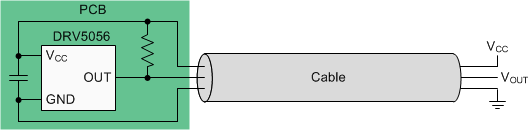 Figure 19. Wire Fault Detection Circuit
Figure 19. Wire Fault Detection Circuit Table 1. Fault Scenarios and the Resulting VOUT
| FAULT SCENARIO | VOUT |
|---|---|
| VCC disconnects | Close to GND |
| GND disconnects | Close to VCC |
| VCC shorts to OUT | Close to VCC |
| GND shorts to OUT | Close to GND |