SBAA551 June 2022 ADS8661 , ADS8665 , ADS8671 , ADS8675 , ADS8681 , ADS8685 , ADS8689 , ADS8691 , ADS8695 , ADS8699 , INA823 , INA826 , LM317L , LM337L , MUX509 , TPS2661 , TPS560430
2.5 Power Supply
The power supply in Figure 2-3 generates three supply voltages (+5 V, –14 V, and +14 V) from a standard PLC field power supply (24 V, ±20%). The +5-V rail for the ADS8689 analog section is generated directly by the TPS560430 buck converter. The negative voltage is created by a discrete charge pump driven from the TPS560430 switch node. The negative voltage LDO LM337 regulates the voltage to –14 V. The LDO LM317L derives the +14-V supply voltage directly from the main +24-V input voltage. The wide +1.65-V to 5-V range for the ADS8689 digital supply is expected to be provided by the host controller power supply (not shown here). However, it is possibly to generate the digital supply voltage from the +5-V rail by a low-voltage LDO such as TLV740P. An isolated power supply design is outside the scope of this document.
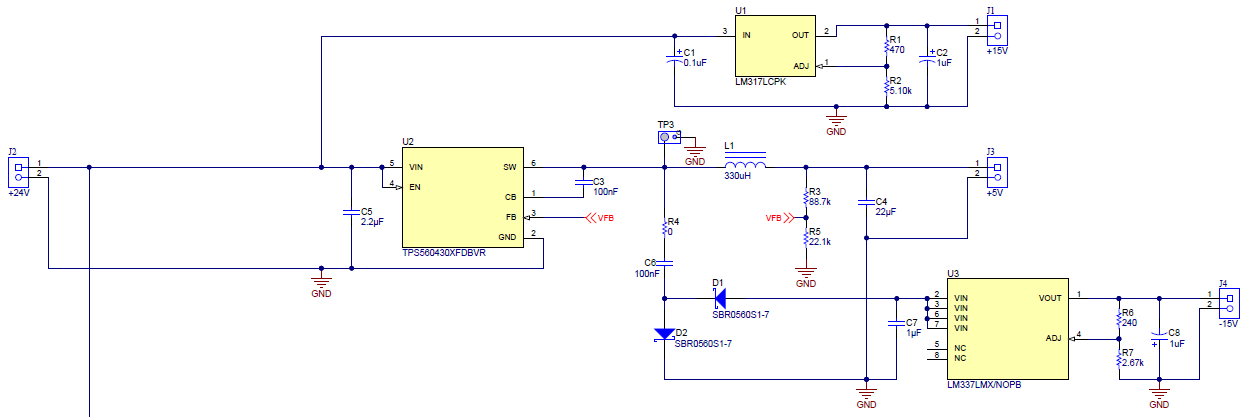 Figure 2-3 Power Supply for Analog Front End
Figure 2-3 Power Supply for Analog Front End