SFFS128 April 2021 LMR36006 , LMR36006-Q1
4 Pin Failure Mode Analysis (Pin FMA)
This section provides a Failure Mode Analysis (FMA) for the pins of the LMR36006 and LMR36006-Q1. The failure modes covered in this document include the typical pin-by-pin failure scenarios:
- Pin short-circuited to Ground (see Table 4-2)
- Pin open-circuited (see Table 4-3)
- Pin short-circuited to an adjacent pin (see Table 4-4)
- Pin short-circuited to supply (see Table 4-5)
Table 4-2 through Table 4-5 also indicate how these pin conditions can affect the device as per the failure effects classification in Table 4-1.
| Class | Failure Effects |
|---|---|
| A | Potential device damage that affects functionality |
| B | No device damage, but loss of functionality |
| C | No device damage, but performance degradation |
| D | No device damage, no impact to functionality or performance |
Figure 4-1 shows the LMR36006 and LMR36006-Q1 pin diagram. For a detailed description of the device pins please refer to the Pin Configuration and Functions section in the LMR36006 and LMR36006-Q1 data sheet.
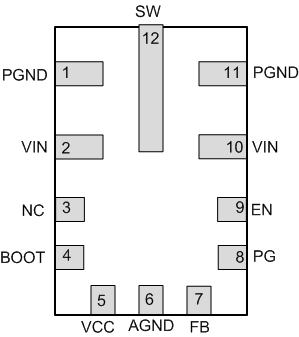 Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram
Figure 4-1 Pin DiagramFollowing are the assumptions of use and the device configuration assumed for the pin FMA in this section:
- Application circuit, as per the LMR36006-Q1 data sheet is used.
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| PGND | 1,11 | This is the ground pin, no effect. | D |
| VIN | 2,10 | No output voltage will be generated. Possible damage to customer input supply, PCB can occur unless customer provides protection, or both. Reverse current from the SW pin to VIN pin, due to discharge of output capacitors, can damage regulator. | B |
| N/C | 3 | No connection when it is NOT used for SW to BOOT connection | D |
| When used for SW to BOOT connection, as recommended, the effect is the same as for pin SW (12). | A | ||
| BOOT | 4 | Driver supply to high side MOSFET will be lost. Output voltage will not be regulated. Possible damage to internal regulator and Cboot charging circuit. | A |
| VCC | 5 | Internal circuits will be disabled. No output voltage will be generated. Possible increase in input current and possible damage to internal LDO. | A |
| AGND | 6 | This is the ground pin, no effect. | D |
| FB | 7 | The regulator will operate at maximum duty cycle. Output voltage will rise to nearly the input voltage level. Possible damage to customer load, output stage components can occur, or both. | D |
| PG | 8 | This is a valid connection for the PG output. PG functionality will be lost. Damage to customer components connected to PG input can occur. | D |
| EN | 9 | This is a valid connection for the EN input. Enable functionality will be lost; the device will remain off with no output voltage generated. Damage to customer components connected to EN input can occur. | B |
| SW | 12 | Shorting the SW pin to ground will result in large currents through the device and subsequent damage. No output voltage will be produced. | A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| PGND | 1,11 | Erratic operation; probable loss of regulation. Possible output voltage increase and damage to customer load | B |
| VIN | 2,11 | Loss of output voltage | B |
| N/C | 3 | No connection when it is NOT used for SW to BOOT connection. | D |
| When used for SW to BOOT connection, as recommended, the effect is the same as for pin BOOT (4). | B | ||
| BOOT | 4 | Driver supply to high side MOSFET will be lost. Output voltage will not be regulated. Low or no output voltage; erratic switching behavior | B |
| VCC | 5 | Internal LDO may oscillate. VCC voltage will not be stable. Internal circuits will not function correctly. Output voltage may not be regulated. | B |
| AGND | 6 | Erratic operation; probable loss of regulation. Possible output voltage increase and damage to customer load | B |
| FB | 7 | Device will not regulate. Output voltage can rise or fall. Damage to customer load, output stage components is probable, or both. | B |
| PG | 8 | This is a valid connection for the PG output. PG functionality will be lost. | B |
| EN | 9 | Loss of enable functionality. Erratic operation; probable loss of regulation | B |
| SW | 12 | Loss of output voltage | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PGND | 1 | VIN | No output voltage will be generated. Possible damage to customer input supply, PCB can occur unless customer provides protection, or both. Reverse current from the SW pin to VIN pin, due to discharge of output capacitors, can damage the regulator. | B |
| VIN | 2 | N/C | No connection when NOT used for SW to BOOT connection. | D |
| When used for SW to BOOT connection, as recommended, the output voltage will rise to the level of VIN. Customer load will be damaged. | B | |||
| N/C | 3 | BOOT | No connection, when NOT used for SW to BOOT connection. | D |
| When used for SW to BOOT connection, as recommended, large currents will flow through internal circuits. Possible damage to internal regulator and CBOOT charging circuits. No output voltage will be produced. |
A |
|||
| BOOT | 4 | VCC | Damage to VCC regulator, other internal circuits, or both. Output voltage can be affected. | A |
| VCC | 5 | AGND | Internal circuits will be disabled. No output voltage will be generated. Possible increase in input current and possible damage to internal LDO | A |
| AGND | 6 | FB | The regulator will operate at maximum duty cycle. Output voltage will rise to nearly the input voltage level. Possible damage to customer load, output stage components can occur, or both. | B |
| FB | 7 | PG | Erratic operation; probable loss of regulation. Possible output voltage increase and damage to customer load | B |
| PG | 8 | EN | Erratic operation; probable loss of regulation. Possible damage to customer circuits connected to these pins | B |
| EN | 9 | VIN | This is a valid connection for the EN input. Enable functionality will be lost; the device will remain on. Damage to customer components connected to EN input can occur. | D |
| VIN | 10 | PGND | No output voltage will be generated. Possible damage to customer input supply, PCB can occur unless customer provides protection, or both. Reverse current from SW pin to VIN pin, due to discharge of output capacitors, can damage the regulator. | B |
| PGND | 11 | SW | Shorting the SW pin to ground will result in large currents through the device and subsequent damage. No output voltage will be produced. | A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| PGND | 1,11 | VOUT = 0 V. Damage to low-side circuitry if PGND >> AGND | A |
| VIN | 2,10 | Normal operation | D |
| N/C | 3 | Normal operation when NOT used for SW to BOOT connection | D |
| Damage to LS FET when used for SW to BOOT connection as recommended. | A | ||
| BOOT | 4 | VOUT = 0 V. CBOOT ESD clamp will run current to destruction. | A |
| VCC | 5 | If VIN exceeds 5.5 V, damage will occur. | A |
| AGND | 6 | VOUT = 0 V. Damage to other pins referred to GND. | A |
| FB | 7 | If VIN exceeds 16 V, damage will occur. VOUT = 0 V. | A |
| PG | 8 | PGOOD ESD clamp will run current to destruction | A |
| EN | 9 | Normal operation | D |
| SW | 12 | Damage to LS FET | A |