SLAA351A April 2007 – November 2018 MSP430F2232 , MSP430F2232 , MSP430F2234 , MSP430F2234 , MSP430F2252 , MSP430F2252 , MSP430F2254 , MSP430F2254 , MSP430F2272 , MSP430F2272 , MSP430F2274 , MSP430F2274
3.4.2 Second Stage of Processing
The second stage of processing does not require a real-time operation. It is done only after 60 ms of the input signal has passed through the first stage of processing. Some of the parameters evaluated during the first stage in conjunction to some new processing are used to complete the process of a glass-breakage detect. Figure 12 shows a flowchart that summarizes the operations.
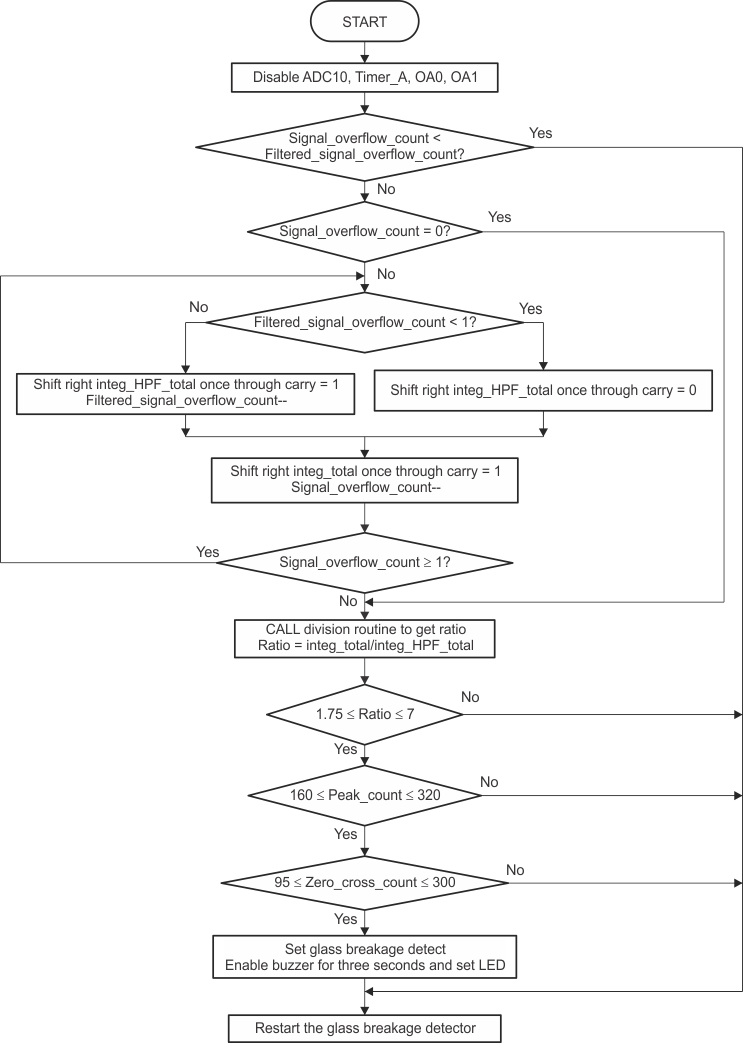 Figure 12. Second Stage Signal Analysis Flowchart
Figure 12. Second Stage Signal Analysis Flowchart