SLAAE72 December 2022 MSPM0L1105 , MSPM0L1106 , MSPM0L1227 , MSPM0L1227-Q1 , MSPM0L1228 , MSPM0L1228-Q1 , MSPM0L1303 , MSPM0L1304 , MSPM0L1304-Q1 , MSPM0L1305 , MSPM0L1305-Q1 , MSPM0L1306 , MSPM0L1306-Q1 , MSPM0L1343 , MSPM0L1344 , MSPM0L1345 , MSPM0L1346 , MSPM0L2227 , MSPM0L2227-Q1 , MSPM0L2228 , MSPM0L2228-Q1
2.2 Power Management (PMU)
The power management unit (PMU) generates the regulated core supplies for the device and provides supervision of the external supply. It also contains a bandgap voltage reference used by the PMU and other analog peripherals.
See from Figure 2-2, the power management unit (PMU) can provides supervision of the external supply, which is a common function in low-power application. Besides, digital and analog peripherals can be dedicated controlled to realize different power levels.
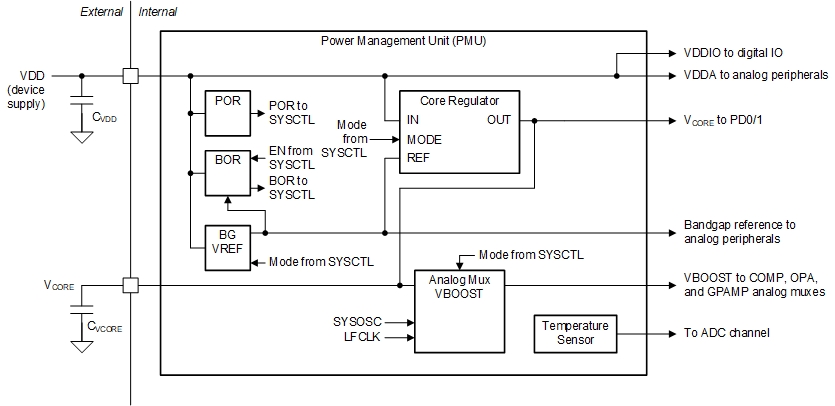 Figure 2-2 MSPM0Lxx PMU Block Diagram
Figure 2-2 MSPM0Lxx PMU Block Diagram