SLLU346 April 2022 SN6507
3 EVM Setup and Operation
Note that this EVM is for operating-parameter evaluation only and not designed for isolation voltage testing. Any voltage applied above the 36-V maximum recommended operating voltage or load current applied above the 500-mA maximum recommended switching current of SN6507 may damage the EVM.
SN6507DGQ is designed to sink a maximum amount of current up to 500 mA through its SW1 and SW2 pins and connect to up to 36 V inputs. Care must be taken to ensure transformer power parameters are not exceeded if they are lower than SN6507 limits.
This section describes the setup and operation of the EVM for parameter-performance evaluation. The EVM is configured for a 24 V input and an unregulated 15 V output. It comes with an SN6507DGQ unit installed in place of U2 and a 24 V IN to 15 V, 500 mA OUT transformer in place of T1. This EVM can also be configured for evaluation of various transformers and voltage input and output combinations by replacing the included push-pull transformer device in place of T1. A list of recommended commercially available transformers is listed in the SN6507 datasheet.
Figure 3-1 shows the basic setup of the EVM with an input power supply needed to evaluate device performance. Power this Evaluation Module by connecting a voltage to VIN that is within the Recommended Operating Range in the SN6507 device datasheet. Typical voltage levels for the VIN are 24 V and 12 V, respectively. Both grounds of the EVM may be shorted together for evaluation. In practice, shorting the non-isolated and isolated grounds would bypass the isolation barrier and is not recommended.
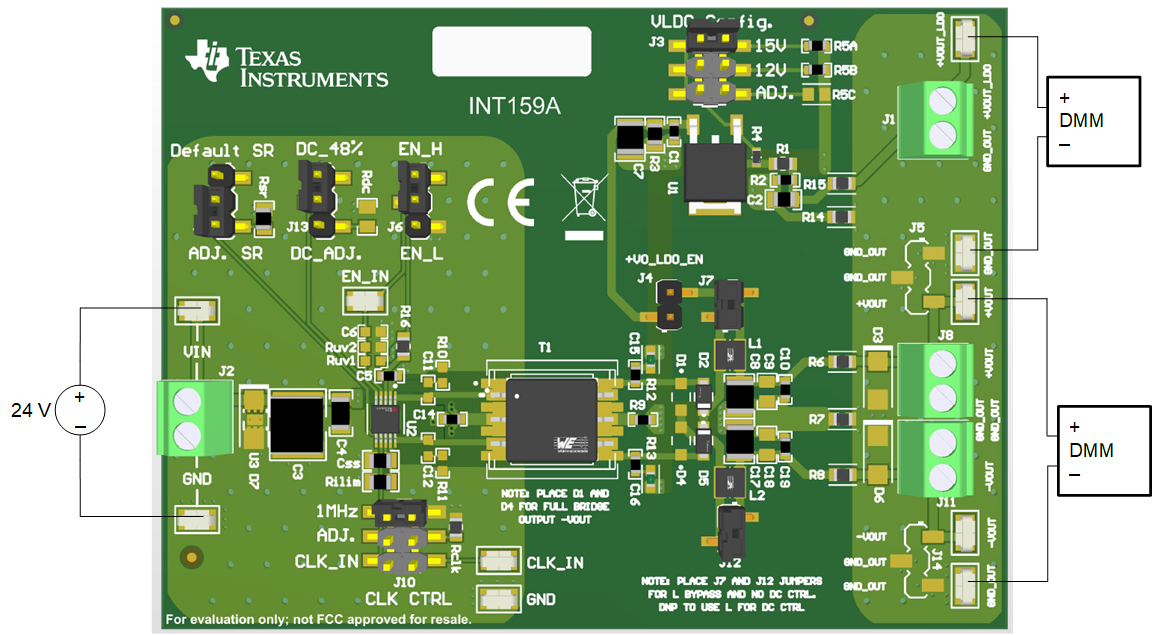 Figure 3-1 Basic SN6507DGQEVM Operation
Figure 3-1 Basic SN6507DGQEVM Operation