SLVAFO8A April 2024 – May 2024 DRV8214 , DRV8234
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction: Need for Sensorless Designs
- 2Ripple Counting − Concept
- 3Case Study: Robotic Wheel Drive
- 4Challenges and Workarounds
- 5Summary
- 6References
- 7Revision History
3.3.2 Soft Start
To protect against high inrush current transients as observed in Section 3.3.1, DRV8214 and DRV8234 have a soft-start feature that allows current to ramp-up to a preset value during the speed and voltage regulation modes. Figure 3-7 demonstrates the performance during soft start.
 Figure 3-7 Performance During Soft
Start
Figure 3-7 Performance During Soft
Start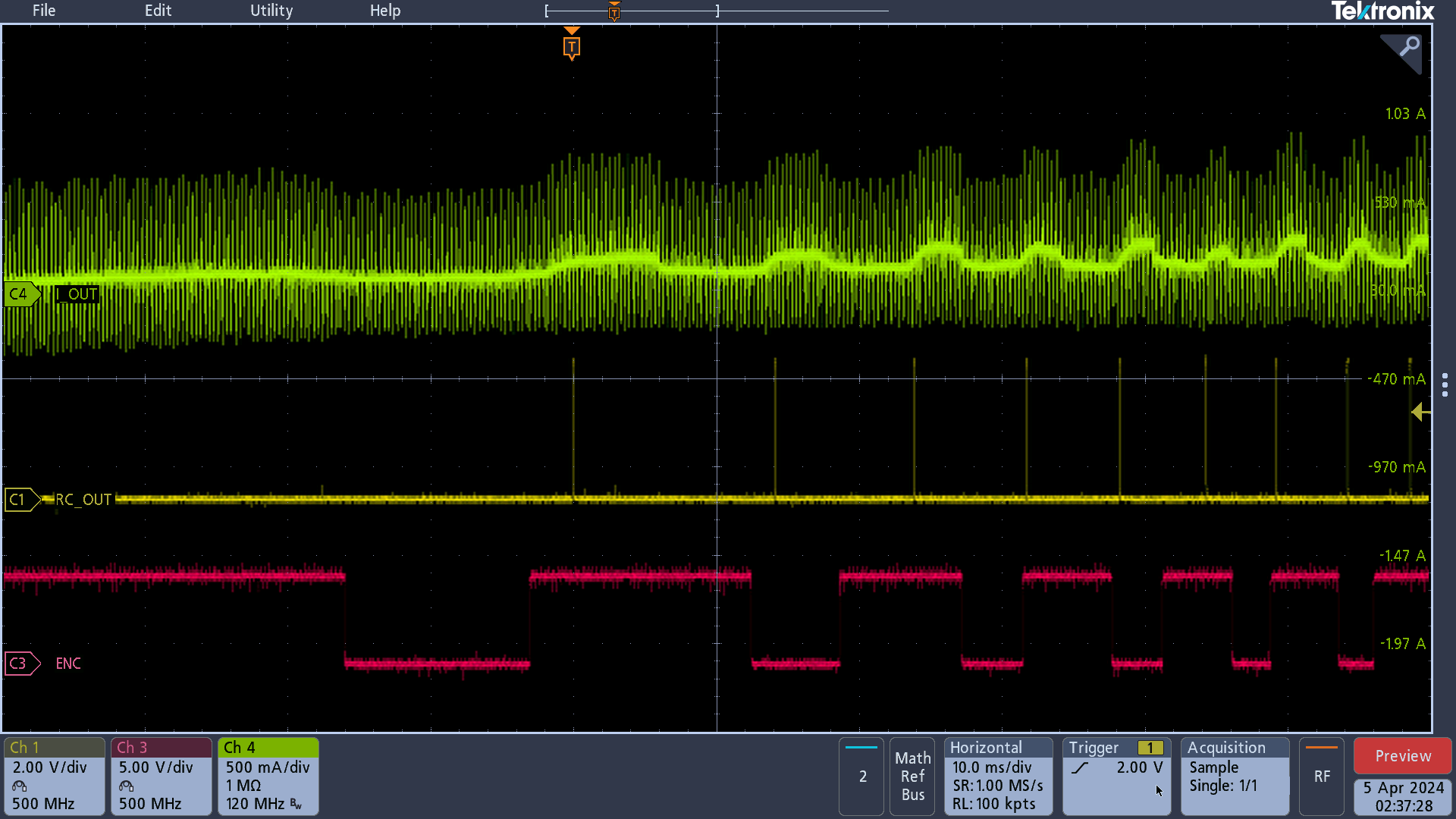 Figure 3-8 Soft Start -
Zoomed
Figure 3-8 Soft Start -
ZoomedFrom Figure 3-7, we can see that all ripples are accurately tracked during soft start. This is validated by the accuracy calculation shown in Table 3-8. Counting is stopped when the motor completes 8 revolutions since the motor current value reaches steady state.
Table 3-8 Accuracy During
Soft-Start
| Parameter | Soft-Start |
|---|---|
| Encoder Counts | 32 |
| RC_OUT Counts | 48 |
| Accuracy | 100% |