SLVUBI2A July 2018 – October 2020 TPS650330-Q1 , TPS650331-Q1
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Requirements
- 3 Operation Instructions
- 4 EVM Configurations
- 5 Test Points
- 6 Graphical User Interface
- 7 Typical Performance Plots
- 8 TPS650330-Q1 EVM Schematic
- 9 TPS650330-Q1 EVM PCB Layers
- 10TPS650330-Q1 EVM Bill of Materials
- 11TPS650330-Q1 Silicon Revision Changes
- 12Revision History
6.2.4.2 Configuring the Power Sequence
The Sequencing Overview tab includes instruments to customize the power sequence of the PMIC. Note that the check boxes are power sequence masks. If a particular logic signal needs to be included as part of the regulator or logic power up sequence, leave the box next to the logic signal unchecked. TI recommends to set Power On Bit unmasked for each rail that is required in the application.
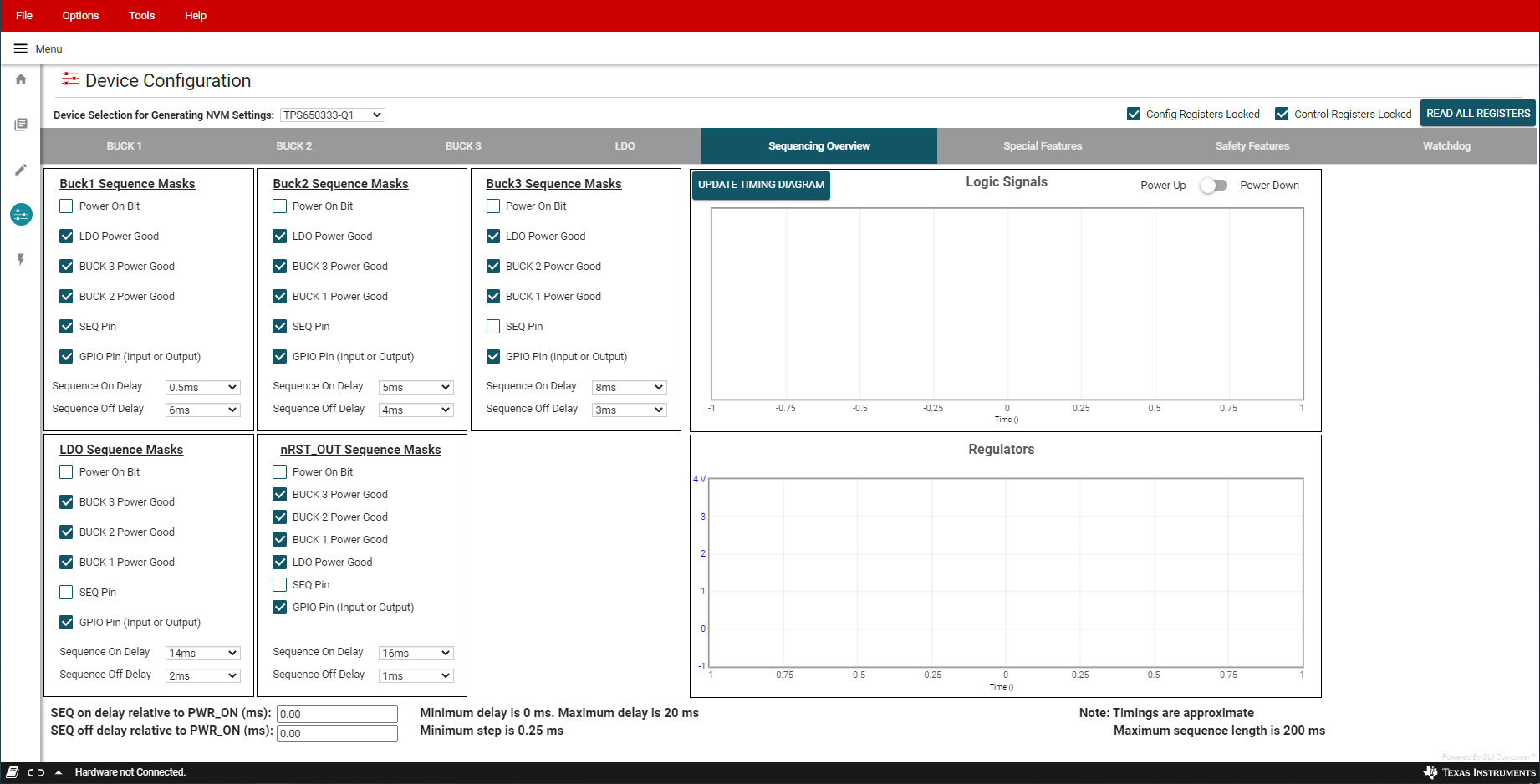 Figure 6-10 Sequencing Overview
Tab
Figure 6-10 Sequencing Overview
Tab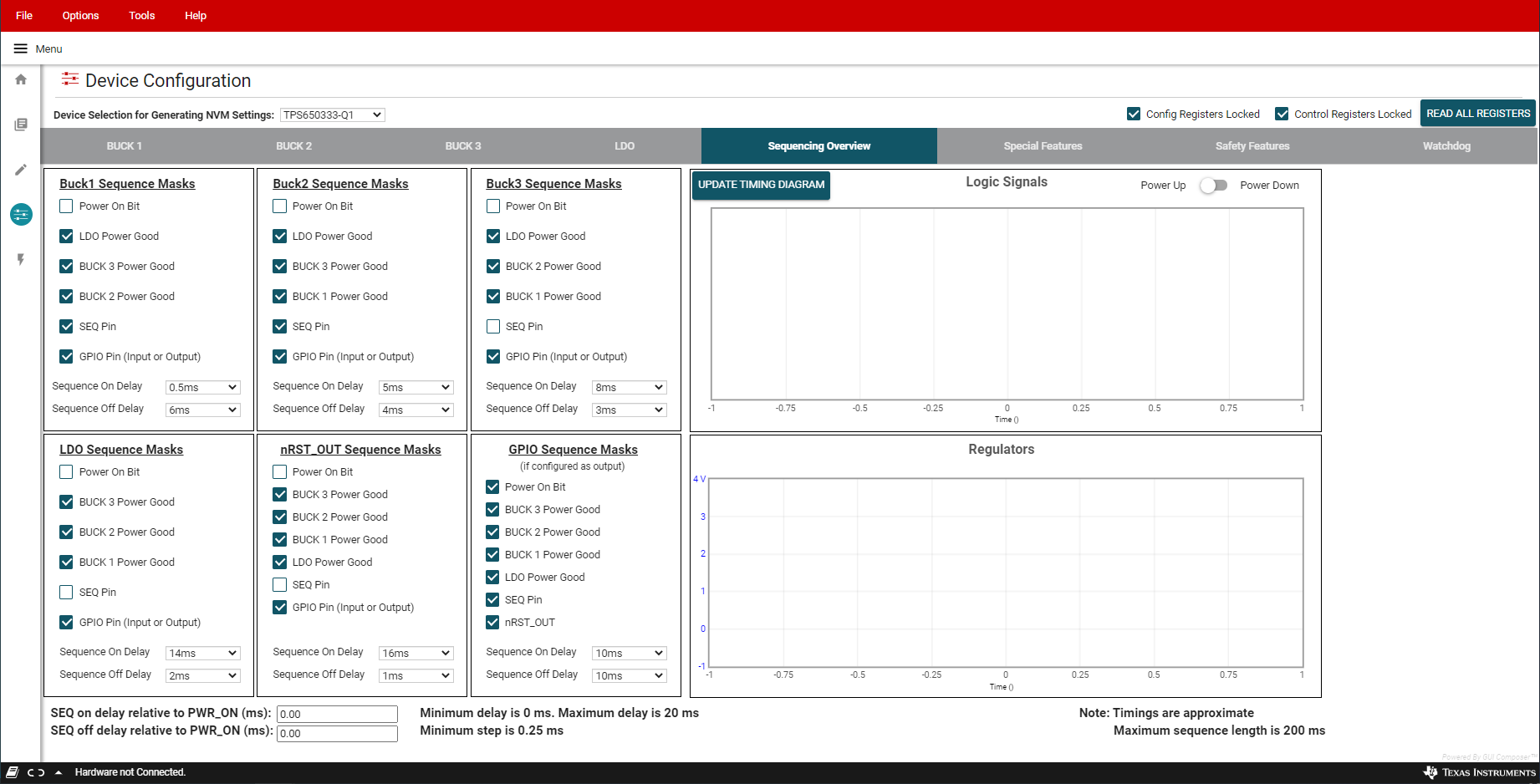 Figure 6-11 Sequencing Overview Including
GPIO
Figure 6-11 Sequencing Overview Including
GPIO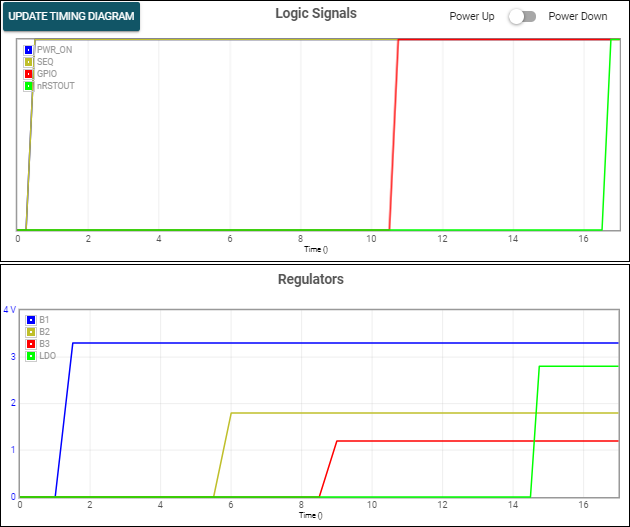 Figure 6-12 GUI Generated Timing Diagram
Figure 6-12 GUI Generated Timing Diagram