SLVUBT8B November 2020 – June 2022 LP8764-Q1 , TPS6594-Q1
- Scalable PMIC's GUI User’s Guide
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Supported Features
- 3 Revisions
- 4 Overview
- 5 Getting Started
- 6 Quick-start Page
- 7 Register Map Page
- 8 NVM Configuration Page
- 9 NVM Validation Page
- 10Watchdog Page
- 11Additional Resources
- 12Appendix A: Troubleshooting
- 13Appendix B: Advanced Topics
- 14Appendix C: Known Limitations
- 15Appendix D: Migration Topics
- 16Revision History
7 Register Map Page
The Register Map page lists the different registers available for configuration. Unlike the Quick-start page, there is no device label to select if multiple PMICs are present. In the case of I2C, the device address is selected in the Device Settings below the Options tab at the top of the GUI. In the case of SPI, the HW connection to the chip select pin will determine which PMIC the GUI communicates with and whose contents are displayed in the Register Map page.
The Register Map page is intended for direct read and writes to the PMIC registers. The read can be done individually or all at once. Similarly, writing to registers can also be all at once or individually. In the Immediate Write mode (option located at the top right of the page), only individual registers are written to immediately with each change in the Field View, change in bits, or change in hexadecimal value. In Deferred Write mode, the writing of a single register or all registers is deferred until the WRITE REGISTER or WRITE ALL REGISTERS button is selected.
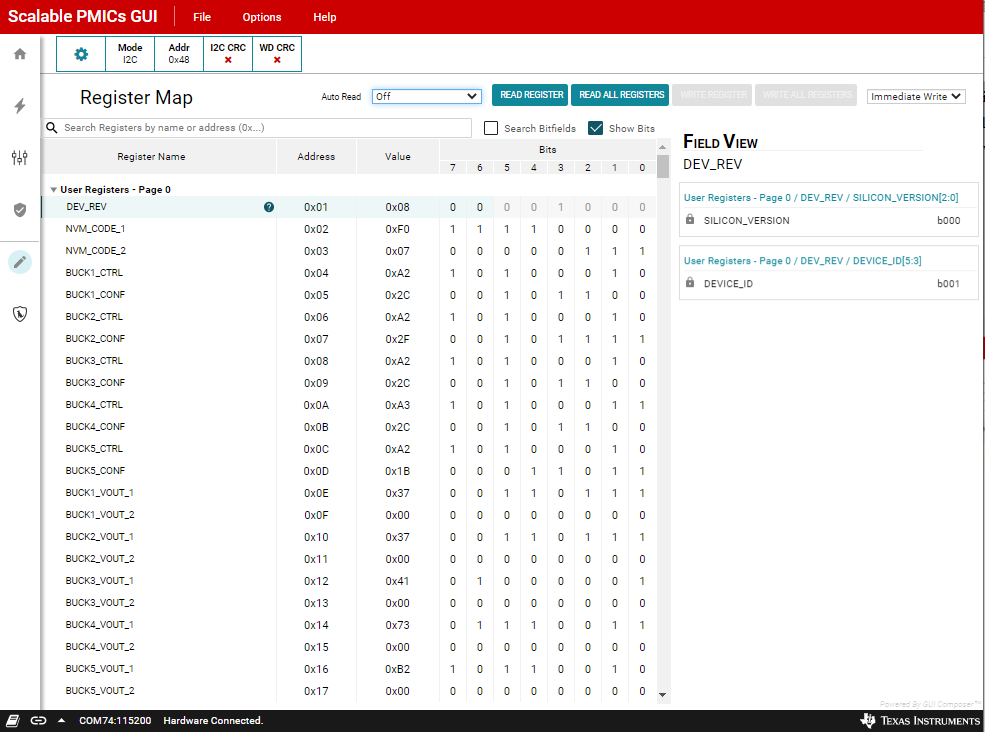 Figure 7-1 Register Map
Figure 7-1 Register MapAlthough visible from the Register Map Page, not all registers can be edited from this page. Specifically, the interface configuration cannot be changed, and similar with the Quick-start page the Buck frequencies cannot be changed. No error is reported, however, with each write is an associated read. The read will update the display so that writes to protected fields will accurately reflect that the write was unsuccessful.