SNVAA30 December 2021 LM5170-Q1
2.4 Implementation of Current Limit
The ISETA pin is analog current programming pin of LM5170-Q1. Figure 2-6 shows the inductor DC current is proportional to the ISETA voltage. VCS_dc is the current sense voltage produced by the shunt resistor RCS1. It has linear relationship with ISETA voltage by Equation 16.
Or by Equation 17.
Or by Equation 18.
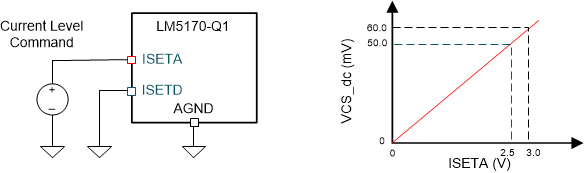 Figure 2-6 ISETA vs VCS_dc Graph of LM5170-Q1
Figure 2-6 ISETA vs VCS_dc Graph of LM5170-Q1To achieve the DC current limit, the ISETA voltage should be clamped. The DC current limit should be determined by maximum allowable load current of 12-V loads in the system. In this example, the maximum load current of the 12-V loads is about 13 A, therefore, VISETA should be clamped at 3.25 V approximately when 5-mΩ shunt resistor is used.
Figure 2-1 includes a simple VISETA clamp circuit consisting of TLV431B-Q1 and two resistor RCC1 and RCC2. The resistor divider ratio sets the clamp voltage level. Note that RCC1 and RCC2 resistance can increase power consumption unnecessarily. In this example, RCC1 = 30.1 kΩ and RCC2 = 18.7 kΩ are used to limit the total power dissipation below 0.22 mW.