SPRUJD3A July 2025 – October 2025 F28E120SB , F28E120SC
- 1
- Read This First
- 1 C2000™ Microcontrollers Software Support
- 2 C28x Processor
-
3 System Control and
Interrupts
- 3.1 Introduction
- 3.2 Power Management
- 3.3 Device Identification and Configuration Registers
- 3.4
Resets
- 3.4.1 Reset Sources
- 3.4.2 External Reset (XRS)
- 3.4.3 Power-On Reset (POR)
- 3.4.4 Brown-Out-Reset (BOR)
- 3.4.5 Watchdog Reset (WDRS)
- 3.4.6 NMI Watchdog Reset (NMIWDRS)
- 3.4.7 Debugger Reset (SYSRS)
- 3.4.8 DCSM Safe Code Copy Reset (SCCRESET)
- 3.4.9 Simulate External Reset (SIMRESET.XRS)
- 3.4.10 Simulate CPU Reset (SIMRESET_CPU1RS)
- 3.5 Peripheral Interrupts
- 3.6 Exceptions and Non-Maskable Interrupts
- 3.7
Clocking
- 3.7.1 Clock Sources
- 3.7.2 Derived Clocks
- 3.7.3 Device Clock Domains
- 3.7.4 XCLKOUT
- 3.7.5 Clock Connectivity
- 3.7.6 Clock Source and PLL Setup
- 3.7.7 Using an External Crystal or Resonator
- 3.7.8 Using an External Oscillator
- 3.7.9 Choosing PLL Settings
- 3.7.10 System Clock Setup
- 3.7.11 SYS PLL Bypass
- 3.7.12 Clock (OSCCLK) Failure Detection
- 3.8 32-Bit CPU Timers 0/1/2
- 3.9 Watchdog Timer
- 3.10 Low-Power Modes
- 3.11 Memory Controller Module
- 3.12 JTAG
- 3.13 System Control Register Configuration Restrictions
- 3.14 Software
- 3.15
SYSCTRL Registers
- 3.15.1 SYSCTRL Base Address Table
- 3.15.2 CPUTIMER_REGS Registers
- 3.15.3 PIE_CTRL_REGS Registers
- 3.15.4 WD_REGS Registers
- 3.15.5 NMI_INTRUPT_REGS Registers
- 3.15.6 XINT_REGS Registers
- 3.15.7 SYNC_SOC_REGS Registers
- 3.15.8 DMA_CLA_SRC_SEL_REGS Registers
- 3.15.9 DEV_CFG_REGS Registers
- 3.15.10 CLK_CFG_REGS Registers
- 3.15.11 CPU_SYS_REGS Registers
- 3.15.12 SYS_STATUS_REGS Registers
- 3.15.13 MEM_CFG_REGS Registers
- 3.15.14 MEMORY_ERROR_REGS Registers
- 3.15.15 ROM_WAIT_STATE_REGS Registers
- 3.15.16 TEST_ERROR_REGS Registers
- 3.15.17 UID_REGS Registers
-
4 ROM Code and Peripheral Booting
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Device Boot Sequence
- 4.3 Device Boot Modes
- 4.4 Device Boot Configurations
- 4.5 Device Boot Flow Diagrams
- 4.6 Device Reset and Exception Handling
- 4.7 Boot ROM Description
- 4.8 Application Notes for Using the Bootloaders
- 4.9 Software
-
5 Dual Code Security Module (DCSM)
- 5.1 Introduction
- 5.2 Functional Description
- 5.3 Flash and OTP Erase/Program
- 5.4 Secure Copy Code
- 5.5 SecureCRC
- 5.6 CSM Impact on Other On-Chip Resources
- 5.7
Incorporating Code Security in User Applications
- 5.7.1 Environments That Require Security Unlocking
- 5.7.2 CSM Password Match Flow
- 5.7.3 C Code Example to Unsecure C28x Zone1
- 5.7.4 C Code Example to Resecure C28x Zone1
- 5.7.5 Environments That Require ECSL Unlocking
- 5.7.6 ECSL Password Match Flow
- 5.7.7 ECSL Disable Considerations for any Zone
- 5.7.8 Device Unique ID
- 5.8 Software
- 5.9 DCSM Registers
-
6 Flash Module
- 6.1 Introduction to Flash and OTP Memory
- 6.2 Flash Bank, OTP, and Pump
- 6.3 Flash Wrapper
- 6.4 Flash and OTP Memory Performance
- 6.5 Flash Read Interface
- 6.6 Flash Erase and Program
- 6.7 Error Correction Code (ECC) Protection
- 6.8 Reserved Locations Within Flash and OTP
- 6.9 Migrating an Application from RAM to Flash
- 6.10 Procedure to Change the Flash Control Registers
- 6.11 Software
- 6.12 FLASH Registers
- 7 Dual-Clock Comparator (DCC)
-
8 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 8.1 Introduction
- 8.2 Configuration Overview
- 8.3 Digital Inputs on ADC Pins (AIOs)
- 8.4 Digital Inputs and Outputs on ADC Pins (AGPIOs)
- 8.5 Digital General-Purpose I/O Control
- 8.6 Input Qualification
- 8.7 GPIO and Peripheral Muxing
- 8.8 Internal Pullup Configuration Requirements
- 8.9 Open-Drain Configuration Requirements
- 8.10 Software
- 8.11 GPIO Registers
- 9 Crossbar (X-BAR)
- 10Direct Memory Access (DMA)
- 11Analog Subsystem
-
12Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 12.1 Introduction
- 12.2 ADC Configurability
- 12.3 SOC Principle of Operation
- 12.4 SOC Configuration Examples
- 12.5 ADC Conversion Priority
- 12.6 EOC and Interrupt Operation
- 12.7 Post-Processing Blocks
- 12.8 Opens/Shorts Detection Circuit (OSDETECT)
- 12.9 Power-Up Sequence
- 12.10 ADC Calibration
- 12.11 ADC Timings
- 12.12 Additional Information
- 12.13
Software
- 12.13.1
ADC Examples
- 12.13.1.1 ADC Software Triggering
- 12.13.1.2 ADC MCPWM Triggering
- 12.13.1.3 ADC Temperature Sensor Conversion
- 12.13.1.4 ADC Continuous Conversions Read by DMA (adc_soc_continuous_dma)
- 12.13.1.5 ADC PPB Offset (adc_ppb_offset)
- 12.13.1.6 ADC PPB Limits (adc_ppb_limits)
- 12.13.1.7 ADC SOC Oversampling
- 12.13.1.8 ADC Trigger Repeater Oversampling
- 12.13.1
ADC Examples
- 12.14 ADC Registers
- 13Comparator Subsystem (CMPSS)
-
14Programmable Gain Amplifier
(PGA)
- 14.1 Programmable Gain Amplifier (PGA) Overview
- 14.2 Linear Output Range
- 14.3 Gain Values
- 14.4 Modes of Operation
- 14.5 External Filtering
- 14.6 Error Calibration
- 14.7 Chopping Feature
- 14.8 Enabling and Disabling the PGA Clock
- 14.9 Lock Register
- 14.10 Analog Front-End Integration
- 14.11 Examples
- 14.12 Software
- 14.13 PGA Registers
-
15Multi-Channel Pulse Width Modulator (MCPWM)
- 15.1 Introduction
- 15.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 15.3 MCPWM Modules Overview
- 15.4 Time-Base (TB) Submodule
- 15.5 Counter-Compare (CC) Submodule
- 15.6 Action-Qualifier (AQ) Submodule
- 15.7 Dead-Band Generator (DB) Submodule
- 15.8 Trip-Zone (TZ) Submodule
- 15.9 Event-Trigger (ET) Submodule
- 15.10 PWM Crossbar (X-BAR)
- 15.11
Software
- 15.11.1
MCPWM Examples
- 15.11.1.1 MCPWM Basic PWM Generation and Updates
- 15.11.1.2 MCPWM Basic PWM Generation and Updates
- 15.11.1.3 MCPWM Basic PWM generation With DeadBand
- 15.11.1.4 MCPWM Basic PWM Generation and Updates without Sysconfig
- 15.11.1.5 MCPWM PWM Tripzone Feature Showcase
- 15.11.1.6 MCPWM Global Load Feature Showcase
- 15.11.1.7 MCPWM DMA Configuration for Dynamic PWM Control
- 15.11.1
MCPWM Examples
- 15.12 MCPWM Registers
-
16Enhanced Capture (eCAP)
- 16.1 Introduction
- 16.2 Description
- 16.3 Configuring Device Pins for the eCAP
- 16.4 Capture and APWM Operating Mode
- 16.5 Capture Mode Description
- 16.6
Application of the eCAP Module
- 16.6.1 Example 1 - Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising-Edge Trigger
- 16.6.2 Example 2 - Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising- and Falling-Edge Trigger
- 16.6.3 Example 3 - Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising-Edge Trigger
- 16.6.4 Example 4 - Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising- and Falling-Edge Trigger
- 16.7 Application of the APWM Mode
- 16.8 Software
- 16.9 ECAP Registers
-
17Enhanced Quadrature
Encoder Pulse (eQEP)
- 17.1 Introduction
- 17.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 17.3 Description
- 17.4 Quadrature Decoder Unit (QDU)
- 17.5 Position Counter and Control Unit (PCCU)
- 17.6 eQEP Edge Capture Unit
- 17.7 eQEP Watchdog
- 17.8 eQEP Unit Timer Base
- 17.9 QMA Module
- 17.10 eQEP Interrupt Structure
- 17.11 Software
- 17.12 EQEP Registers
-
18Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 18.1 Introduction
- 18.2 Functional Description
- 18.3 Initialization and Configuration
- 18.4 Software
- 18.5 UART Registers
-
19Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 19.1 Introduction
- 19.2 System-Level Integration
- 19.3 SPI Operation
- 19.4 Programming Procedure
- 19.5 Software
- 19.6 SPI Registers
-
20Inter-Integrated Circuit Module (I2C)
- 20.1 Introduction
- 20.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 20.3
I2C Module Operational Details
- 20.3.1 Input and Output Voltage Levels
- 20.3.2 Selecting Pullup Resistors
- 20.3.3 Data Validity
- 20.3.4 Operating Modes
- 20.3.5 I2C Module START and STOP Conditions
- 20.3.6 Non-repeat Mode versus Repeat Mode
- 20.3.7 Serial Data Formats
- 20.3.8 Clock Synchronization
- 20.3.9 Clock Stretching
- 20.3.10 Arbitration
- 20.3.11 Digital Loopback Mode
- 20.3.12 NACK Bit Generation
- 20.4 Interrupt Requests Generated by the I2C Module
- 20.5 Resetting or Disabling the I2C Module
- 20.6 Software
- 20.7 I2C Registers
-
21Serial Communications Interface (SCI)
- 21.1 Introduction
- 21.2 Architecture
- 21.3 SCI Module Signal Summary
- 21.4 Configuring Device Pins
- 21.5 Multiprocessor and Asynchronous Communication Modes
- 21.6 SCI Programmable Data Format
- 21.7 SCI Multiprocessor Communication
- 21.8 Idle-Line Multiprocessor Mode
- 21.9 Address-Bit Multiprocessor Mode
- 21.10 SCI Communication Format
- 21.11 SCI Port Interrupts
- 21.12 SCI Baud Rate Calculations
- 21.13 SCI Enhanced Features
- 21.14 Software
- 21.15 SCI Registers
- 22Revision History
3.7.12.1 Missing Clock Detection
The missing clock detect (MCD) logic detects OSCCLK failure, using SECCLK as the reference clock source. This circuit only detects complete loss of OSCCLK and doesn’t do any detection of frequency drift on the OSCCLK.
This circuit monitors the OSCCLK (primary clock) using the clock provided by the SECCLK (secondary clock) as a backup clock. This circuit functions as below:
- The primary clock (OSCCLK) clock keeps ticking a 7-bit counter (named as MCDPCNT). This counter is asynchronously reset with XRSn.
- The secondary clock (SECCLK) clock keeps ticking a 13-bit counter (named as MCDSCNT). This counter is asynchronously reset with XRSn.
- Each time MCDPCNT overflows, the MCDSCNT counter is reset. Thus, if OSCCLK is present or not slower than SECCLK by a factor of 64, MCDSCNT never overflows.
- If OSCCLK stops for some reason or is slower than SECCLK by at least a factor of 64, the MCDSCNT overflows and a missing clock condition is detected on OSCCLK.
- The above check is continuously active, unless the MCD is disabled using MCDCR register (by making the MCLKOFF bit 1).
- If the circuit ever detects a missing
OSCCLK, the following occurs:
- The MCDSTS flag is set.
- The MCDSCNT counter is frozen to prevent further missing clock detection.
- The CLOCKFAIL signal goes high, which generates TRIP events to PWM modules and sends NMIs to CPU1.NMIWD.
- PLL is forcefully bypassed and OSCCLK source is switched to SECCLK (New, System Clock Frequency = SECCLK Freq 10MHz)/SYSDIV). In the meantime when the clock switches to SECCLK, the System runs on PLL limp Clock.
- SYSPLLMULT.IMULT is zeroed out automatically in this case.
- While the MCDSTS bit is set, the OSCCLKSRCSEL bits have no effect and OSCCLK is forcefully connected to SECCLK.
- PLLRAWCLK going to the system is switched to SECCLK automatically.
- If the MCLKCLR bit is written (this is a W=1 bit), MCDSTS bit is cleared and OSCCLK source is decided by the OSCCLKSRCSEL bits. Writing to MCLKCLR also clears the MCDPCNT and MCDSCNT counters to allow the circuit re-evaluate missing clock detection. If user wants to lock the PLL after missing clock detection, switch the clock source to SECCLK (using OSCCLKSRCSEL register), do a MCLKCLR and re-lock the PLL.
- The MCD is enabled at power up.
Figure 3-10 shows the missing clock logic functional flow.
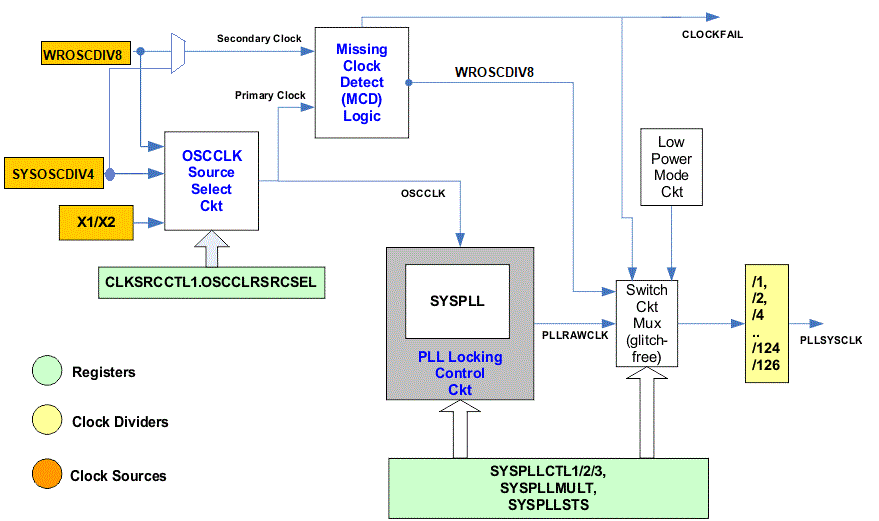 Figure 3-10 Missing Clock Detection Logic
Figure 3-10 Missing Clock Detection LogicNote:
- When XTAL is primary clock, SYSOSCDIV4 can be selected as secondary clock as this clock is more accurate than WROSCDIV8.
- On a complete clock failure when OSCCLK is not operating, the operation can take a maximum time of 8192 SECCLK cycles (that is, 0.8192ms) before the CLOCKFAIL signal goes high, after which:
- NMI is generated
- OSCCLK is switched to SECCLK
- PWM Trip happens