TIDT256A March 2022 – March 2022
3.3 SEPIC Load Transients
Load transient response is shown in the following figures.
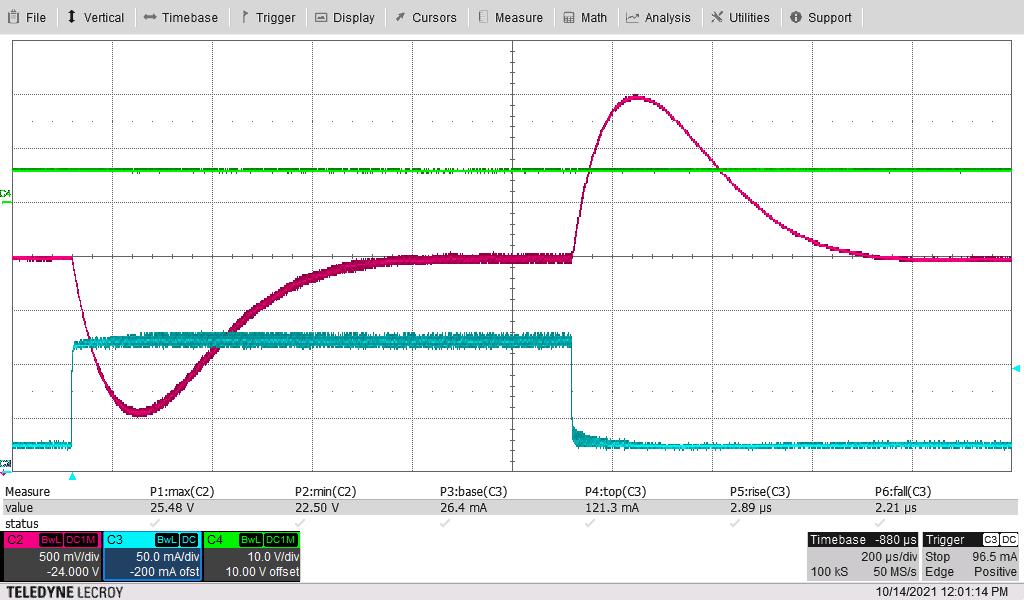
Green = VIN, Pink = VOUT, Blue = Load Current
Figure 3-7 Load Transients, , VIN = 6 V, Switching Frequency = 445 kHz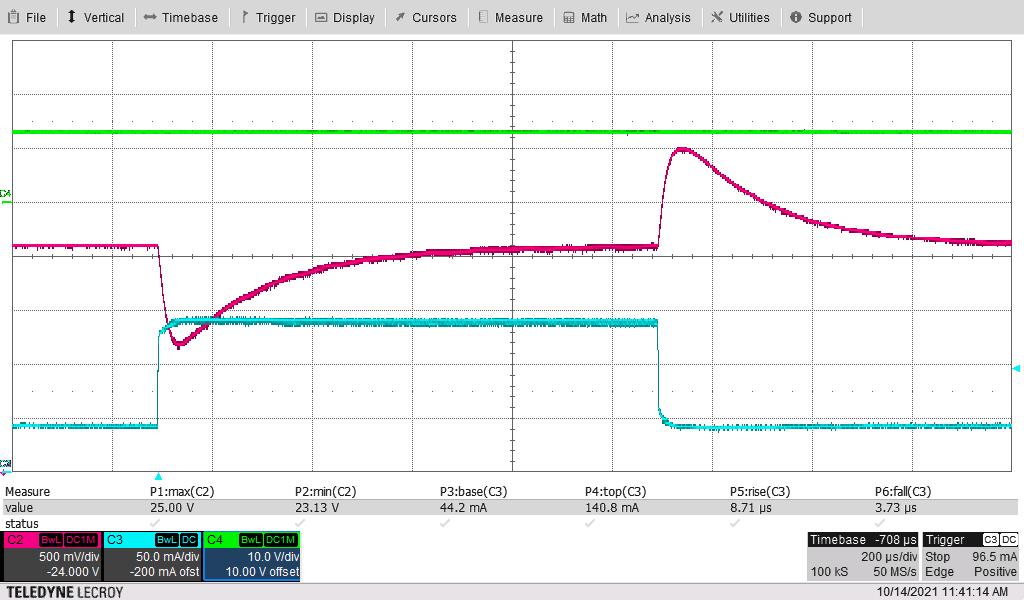
Green = VIN, Pink = VOUT, Blue = Load Current
Figure 3-9 Load Transient, VIN = 13 V, Switching Frequency = 2 MHz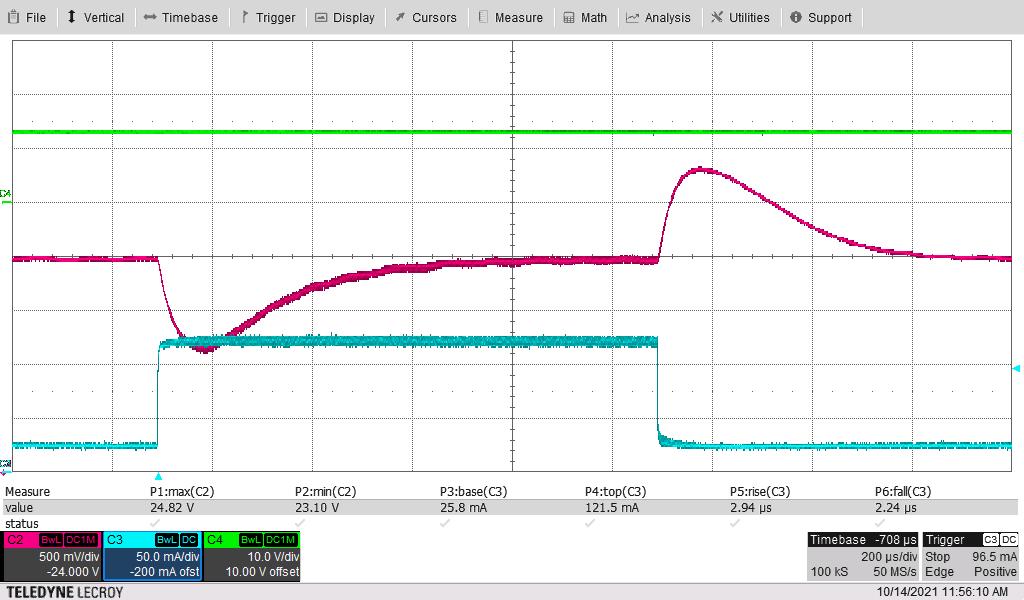
Green = VIN, Pink = VOUT, Blue = Load Current
Figure 3-8 Load Transient, VIN = 13 V, Switching Frequency = 445 kHz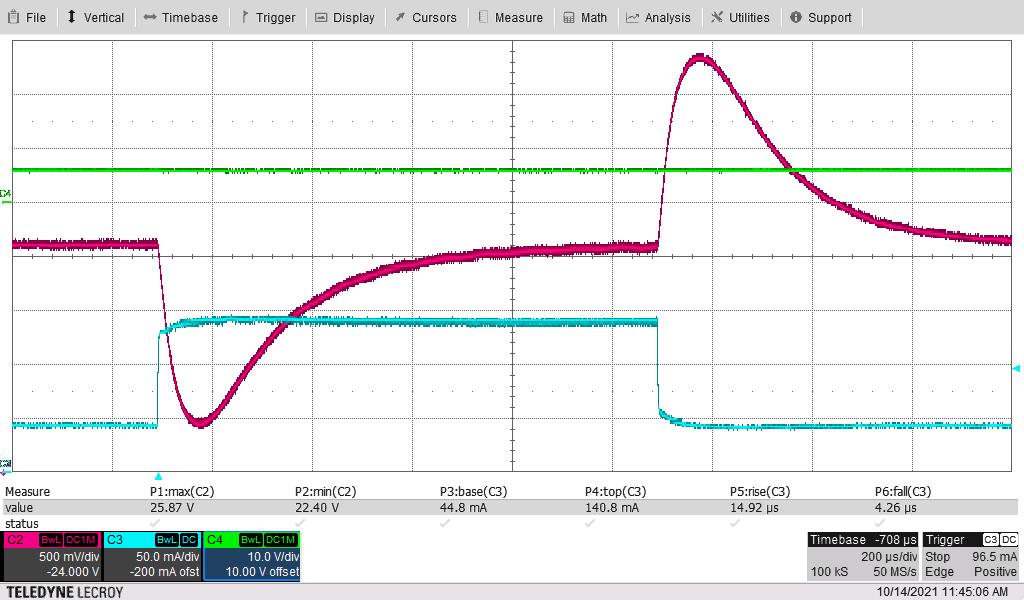
Green = VIN, Pink = VOUT, Blue = Load Current
Figure 3-10 Load Transient, VIN = 6 V, Switching Frequency = 2 MHz