TIDT293 October 2022
3.9 Low- and High-Level Adjust
The low- and high-level adjustment is made by turning the potentiometers R15 and R23, respectively. Make sure the levels along with the pulse width and period meet the SOA ratings of the FET (Q2).
The following scope plot is a 1-A to 100-A load transient for a 100-V output. The results in the following image use a PSMN035-125B MOSFET in the 100-A, 100-V variant.
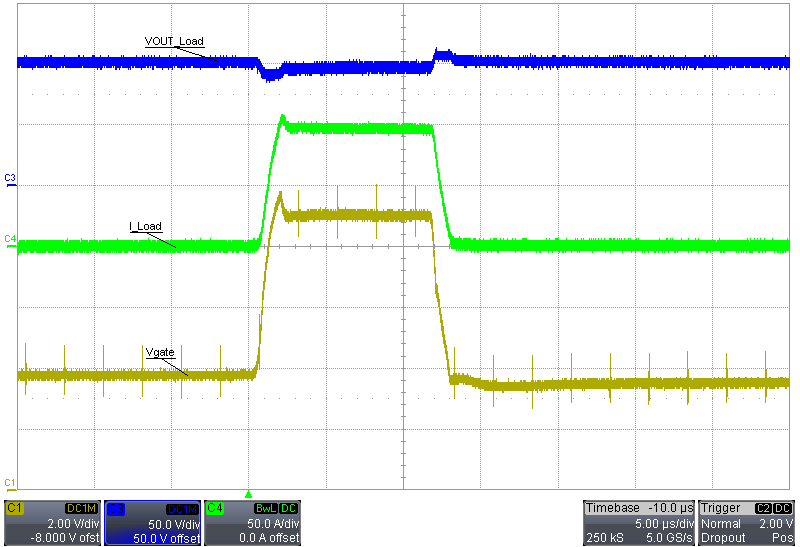 Figure 3-17 PSMN035-150B 100-V Output, 1-A to 100-A Load Transient
Figure 3-17 PSMN035-150B 100-V Output, 1-A to 100-A Load TransientThe following scope plot is a 10-A to 25-A load transient for a load of 10 V. The results in the following waveform use a PSMN008-75B MOSFET in the 125-A, 50-V variant.
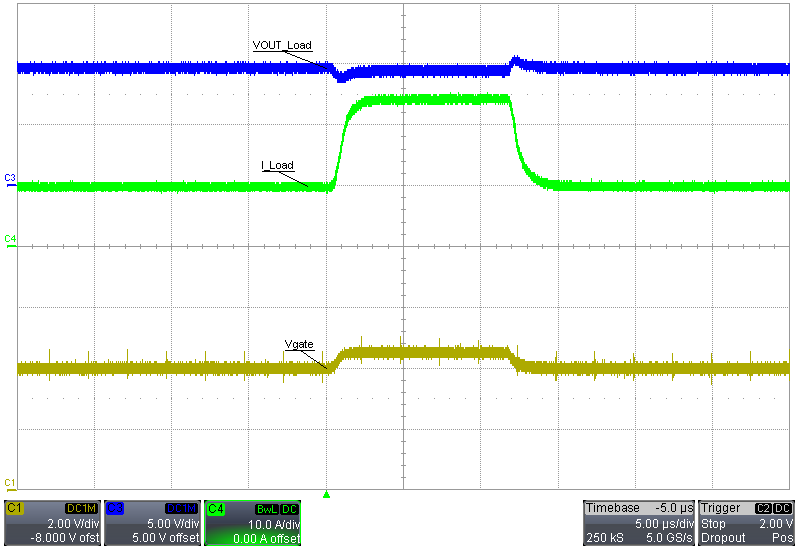 Figure 3-18 PSMN008-75B, 10-V Output, 10-A to 25-A Load Transient
Figure 3-18 PSMN008-75B, 10-V Output, 10-A to 25-A Load Transient