TIDT293 October 2022
3.11 Period and Delay Adjust
The period adjustment is made by turning the potentiometer R36. Jumpers J8 and J9 can be installed to set the range of period adjustment. Periods range from a minimum of 11 ms and maximum of 160 ms.
The delay adjustment is made by turning the potentiometer R46. Jumpers J10 and J11 can be installed to set the range of delay adjustment. The delay ranges depend on the adjusted period.
The following scope plots are load transients of a 1-A to 5-A step at 5 V with a combination of minimum and maximum times for the period and delay.
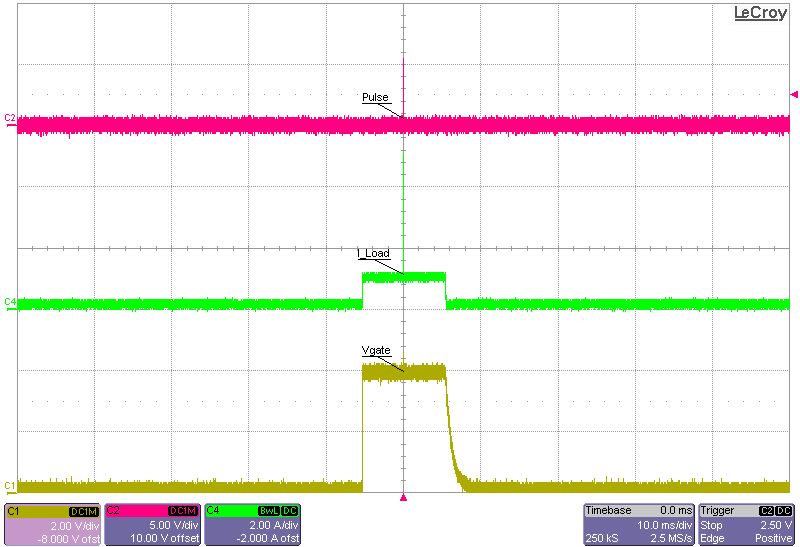 Figure 3-21 Minimum Delay and Minimum
Period 11 ms
Figure 3-21 Minimum Delay and Minimum
Period 11 ms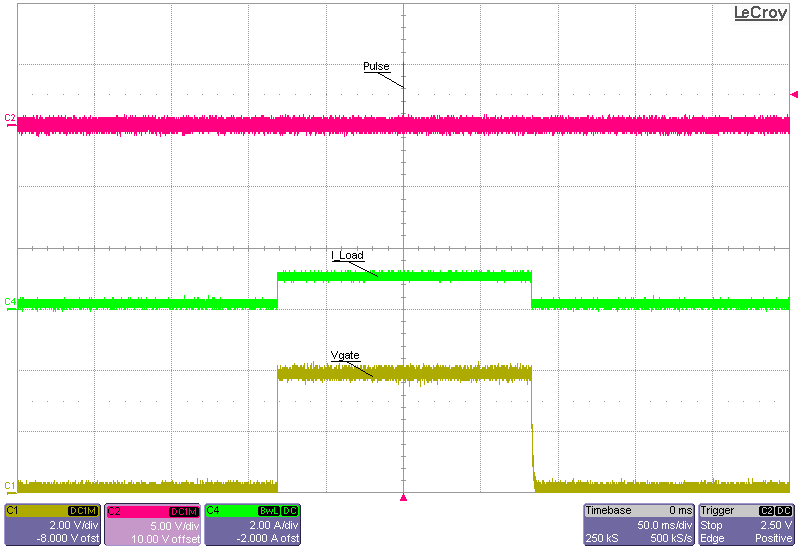 Figure 3-22 Maximum Delay and Maximum
Period 160 ms
Figure 3-22 Maximum Delay and Maximum
Period 160 msHaving a large delay with a small a period causes a mistiming between the high-level step and the low-level step. The load transient does not occur because of this mistiming. Adjust the period and delay simultaneously to avoid this mistiming.
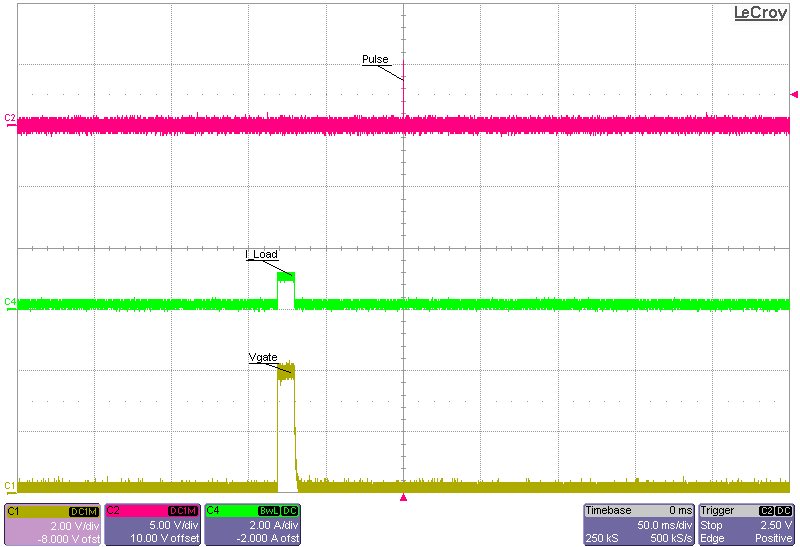 Figure 3-23 Maximum Delay and Minimum
Period Mistiming
Figure 3-23 Maximum Delay and Minimum
Period Mistiming