TIDUEU6B September 2020 – December 2021 OPA810
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design Files
- 5Software Files
- 6Related Documentation
- 7Revision History
2.3.2 Proposed Design
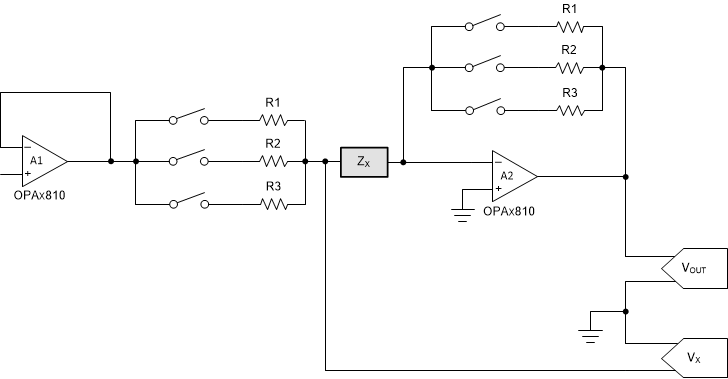 Figure 2-6 Impedance Measurement Design
Figure 2-6 Impedance Measurement DesignIn this method, three different combinations of RG – RF (labeled as R1, R2 & R3 in Figure 2-6) are selected for three ranges of impedance ZX. The ranges can be seen in Table 2-1. The architecture in this method is very similar to the existing architecture explained in last section. The only difference is that the RG is added in series with ZX. Also the value of RG is equal to RF. The stability analysis in Section 2.3.2.1 explains the advantage of this kind of setting.