DLPA078B February 2017 – September 2021 DLP160AP , DLP160CP , DLP2000 , DLP2010 , DLP230GP , DLP230KP , DLP230NP , DLP3010 , DLP3310 , DLP4710 , DLP471TP , DLPC3420 , DLPC3421
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction to Optical Modules
- 2 Use Case Considerations
- 3 Core Optical Module Specifications
- 4 Additional Optical Module Specifications
- 5 Features Implemented in Software
- 6 Hardware Integration Considerations
- 7 Business Considerations
- 8 Example Optical Module Specification Table
- 9 Get Started with Development
- 10Revision History
3.6 Offset
Offset describes the path of the projected light once it exits the projection lens. 0% offset describes an optical module that sends light equally up and down after it exits the projection lens. 100% offset describes an optical module that sends the top of the image up and keeps the bottom of the image coincident with the projection lens axis. 100% or higher (i.e. tilted up) offset is most common in order to avoid sending the bottom part of a projected image into the surface on which the product is resting. However, 0% offset may be preferred for some applications and 0% offset optical designs allow for thinner optical modules.
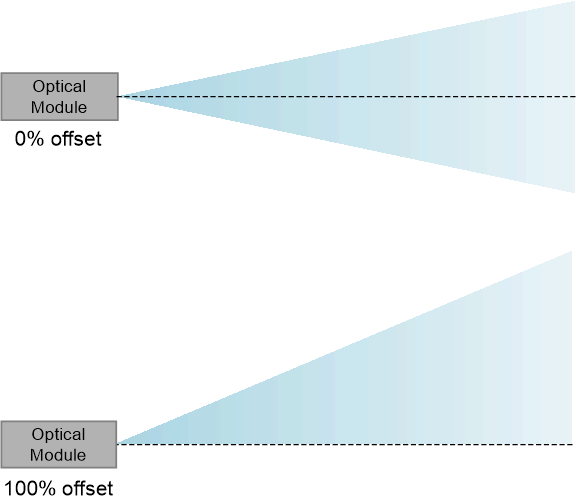 Figure 3-4 0% Offset and 100% Offset
Figure 3-4 0% Offset and 100% Offset