DLPU102B December 2020 – July 2022
- Read This First
- 1DLP LightCrafter Dual DLPC900 EVM Overview
- 2Quick Start
-
3Operating the DLP LightCrafter Dual DLPC900 EVM
- 3.1 DLP LightCrafter Dual DLPC900 Control Software
- 3.2 PC Software
- 3.3 System Common Controls
- 3.4 System Settings
- 3.5 Video Mode
- 3.6
Pattern Modes
- 3.6.1 Menu Bar
- 3.6.2 Creating a Pattern Sequence in Pattern On-The-Fly Mode
- 3.6.3 Creating a Pattern Sequence in Pre-Stored Pattern Mode
- 3.6.4 Reordering a Pattern Sequence using the Edit LUT Feature
- 3.6.5 Creating a Pattern Sequence in Video Pattern Mode
- 3.6.6 Creating a Pattern Sequence With DMD Block Load
- 3.6.7 Pattern Settings
- 3.7 Batch Files
- 3.8 Peripherals
- 3.9 Firmware
- 3.10 Flash Device Parameters
- 3.11 JTAG Flash Programming
- 3.12 Intel (Altera) FPGA Programming
- 4Connectors
- 5Power Supply Requirements
- 6Safety
- 7Revision History
3.8 Peripherals
Click the Peripherals button at the top of the GUI to display the Peripherals panel as shown in Figure 4-19.
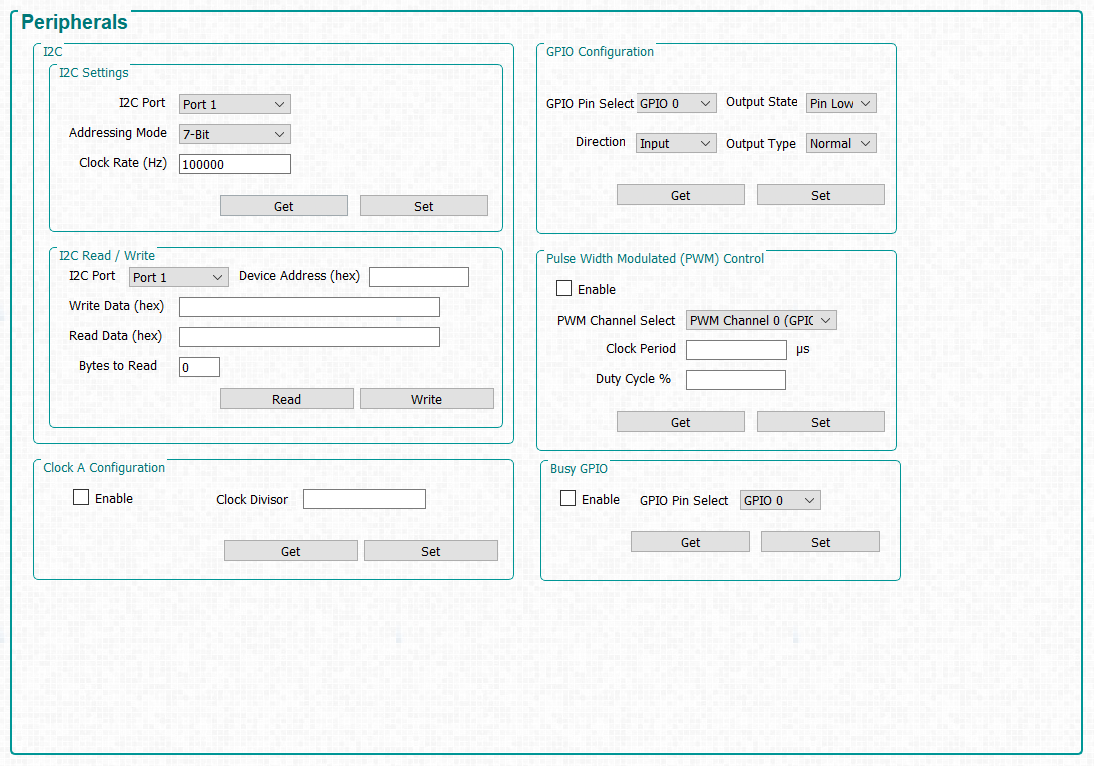 Figure 3-19 Peripherals Panel
Figure 3-19 Peripherals Panel- The I2C group box allows external I2C device to be controlled using one of the DLPC900 I2C interfaces. For example, if an LED driver requires I2C communications to enable the LEDs, then a command can be sent to the LED driver using this interface. When using the I2C interfaces, first configure the I2C port using the commands within the I2C Settings and then perform data transfers using the commands within the I2C Read/Write.
- The Clock A Configuration group box allows the user to enable and control the output frequency of OCLKA. The clock can be used as a source to some external logic.
- The GPIO Configuration group box allows the user to configure any of the nine available GPIOs. These GPIOs can be configured as inputs or outputs.
- The Pulse Width Modulate Control group box allows a user to configure any of the four available PWM outputs.
Note:
GPIO_PWM_00 – GPIO_PWM_03 are shared GPIO\PWM outputs.