SBAS350G June 2005 – January 2021 ADS1232 , ADS1234
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Analog Inputs (AINPX, AINNX)
- 8.3.2 Temperature Sensor (ADS1232 Only)
- 8.3.3 Low-Noise PGA
- 8.3.4 Voltage Reference Inputs (REFP, REFN)
- 8.3.5 Clock Sources
- 8.3.6 Digital Filter Frequency Response
- 8.3.7 Settling Time
- 8.3.8 Data Rate
- 8.3.9 Data Format
- 8.3.10 Data Ready and Data Output (DRDY/DOUT)
- 8.3.11 Serial Clock Input (SCLK)
- 8.3.12 Data Retrieval
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.4.5 Power-Up Sequence
When powering up the ADS123x, follow the prescribed PWDN pin sequence as shown in Figure 8-15. At power-up, hold the PWDN pin low until after AVDD and DVDD have stabilized above the minimum specified voltage levels. After an initial delay where PWDN must be held low (t15), take PWDN high then toggle PWDN low to high with pulse durations (t16 and t17) as shown in Figure 8-15 and Table 8-13. The ADC then begins operation as shown in Figure 8-14 and Table 8-12. Control PDWN by the host processor to provide the required power-on timing.
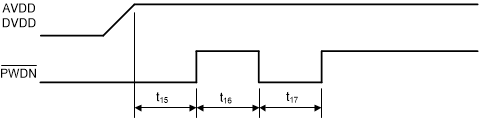 Figure 8-15 Power-Up
Timing Sequence
Figure 8-15 Power-Up
Timing SequenceTable 8-13 Power-up Timing Requirements
for Figure 8-15
| PARAMETER | MIN(1) | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| t15 | Delay time, PWDN high after AVDD, DVDD stable | 10 | µs | |
| t16 | Pulse duration, PWDN high | 26 | µs | |
| t17 | Pulse duration, PWDN low | 26 | µs | |
(1) fCLK = 4.9152 MHz. For fCLK < 4.9152
MHz, adjust the PWDN delay time and pulse duration
accordingly.